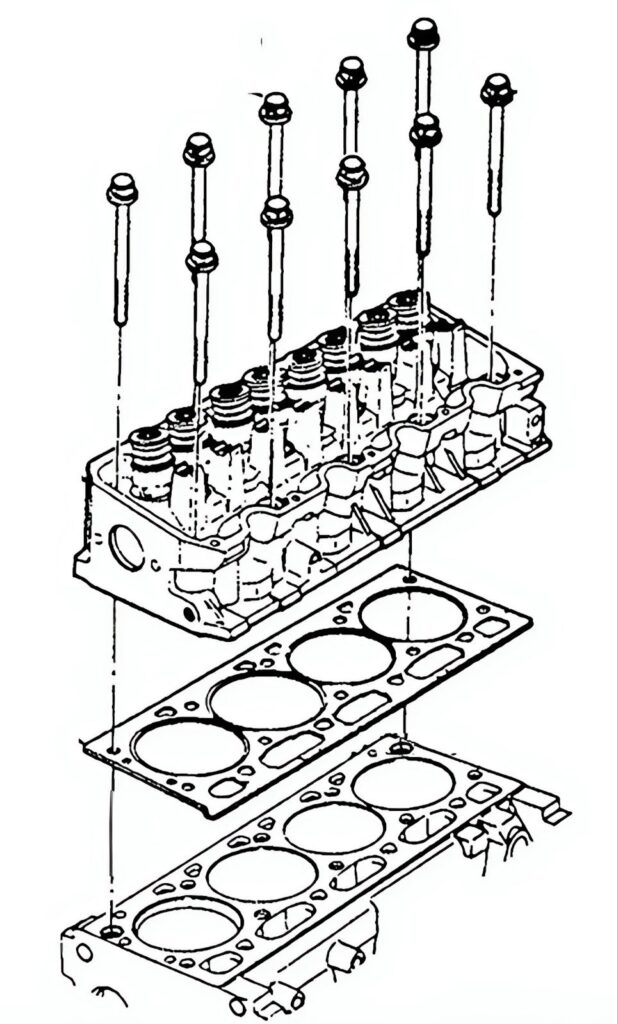
Head gaskets are responsible for sealing the gap between the engine block and the cylinder head and containing the intense heat of combustion at the perimeter of each cylinder.
This means some parts of the head gasket directly line the combustion chamber, as well as oil and coolant lines. Head gaskets need to be made of a durable material that can handle tremendous temperatures and pressures. A compromised head gasket often results in oil or coolant leaks, which can cause your engine to overheat or catch fire.
Head Gasket Materials
Head gaskets are primarily made from four materials:
Multi-layer Steel
Practically all vehicles have multi-layer steel gaskets. These gaskets use multiple steel layers that are joined together with a special adhesive. Multi-layer steel gaskets can have anywhere from two to five layers, depending on their application. This type of gasket is the most popular because it can endure higher pressure compared to other types of head gaskets. Multi-layer steel gaskets can even be used in high-performance engines.

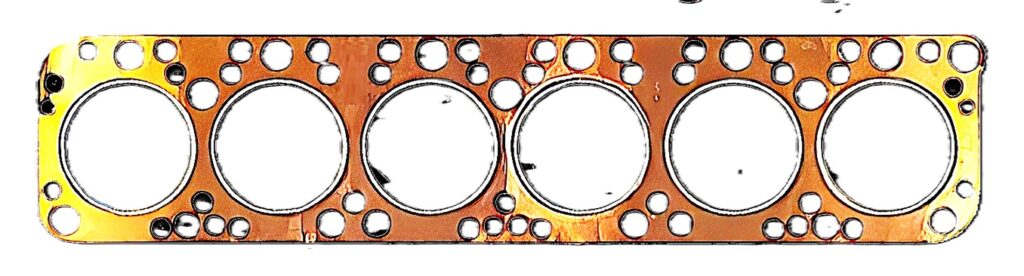
Copper
Copper head gaskets can be used in high-performance applications that need extra sealing from a lot of compression. Some older Diesel engines had reusable copper head gaskets.
No gasket material protects against leakages better than solid copper. However, copper head gaskets require extra steps to be safely fitted into vehicles. Mechanics will need a special machine called an o-ringing device so that the engine block or cylinder head can fit the necessary o-rings for copper head gaskets. The added installation steps mean switching from a composite or multi-layer head gasket won’t be straightforward.
Composite
Composite head gaskets are made from graphite. It’s still a strong material for head gaskets, but other materials simply offer better protection from leaks. As a result, most vehicle manufacturers simply don’t use composite head gaskets anymore.

Elastomeric
An elastomeric head gasket uses a flat hardened steel sheet coated with an elastomeric compound similar to rubber. Silicone elastomer-based materials like rubber, silicone foam, fluorosilicone, silicone sponge, and cellular urethane can be used for elastomeric gaskets. These rubber-like materials allow these gaskets to seal the two mating surfaces even when they aren’t completely flat. This flexibility boosts seal effectiveness and eliminates the possibility of leaks.
How to Choose the Right Material For Your Application
A blown head gasket is a problem you would want to avoid because it can lead to engine damage, which is incredibly expensive and labor-intensive to fix. Head gasket material choice is critical in avoiding such problems. So what is the best head gasket material? The answer is it depends on your application. All head gaskets are engineered to be durable, but some materials are known to be more durable than others.
If you’re looking for durability, then going for a multi-layer steel gasket is a safe bet. Copper is even better. If you have a high-performance engine that has high compression ratios, it would also be best to go for a copper head gasket. However, the added steps in installing copper head gaskets might not be worth it. Elastomeric head gaskets are also good, as they’re known to provide a good seal. However, it’s also known that they don’t last as long as other head gaskets. Overall, if you’re not searching after every marginal gain for your engine, the best head gasket material might just be whatever you can find at your local auto shop.
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.