Your car contains a wide range of fuses, including fuses for the alternator. The primary alternator fuse (or fusible link) will blow whenever there’s excessive current flow due to a short circuit or other malfunction.
When the primary alternator fuse blows, the charging system will no longer work as it should—and you’ll begin to notice a variety of problems.

As you might know, the alternator charges the battery and supplies electricity to the vehicle whenever the engine is running. The alternator is driven off the engine by a belt, which allows the alternator to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy through magnetic induction.
Most of the time, there’s a high-amperage fuse or fusible link between the alternator’s battery terminal and the battery. Also, there are usually low-amperage fuses in series with the alternator’s sense terminal and ignition terminal.
What Is an Alternator Fuse?
But when someone mentions the “alternator fuse”, they’re generally referring to the primary, high-amperage fuse (or fusible link) between the alternator and the battery.
Like any fuse, the primary alternator fuse acts as a circuit protection device. When there’s excessive current flow, the fuse blows to prevent a circuit overload that could lead to melted wires, damaged components—and a potential fire.
Your car has several fuses, including one for the alternator, which helps charge the battery and power the vehicle when the engine is running. The primary alternator fuse (or fusible link) blows if there is too much current, often due to a short circuit or malfunction. When this fuse blows, the charging system stops working properly, leading to various problems.
The alternator is powered by the engine via a belt and converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. There are also smaller fuses connected to other parts of the alternator system, but the primary fuse is the key one between the alternator and the battery. This fuse acts as a safety device, preventing overloads that could damage parts or cause fires. Replacing the blown fuse restores the alternator’s function.
Signs of a Bad Alternator Fuse or Fusible Link
It’s important to point out that alternator fuses do NOT blow for no reason. If your car’s alternator fuse is blown, that means there’s a problem you need to address.
The only exception is if the vehicle has been worked on or jump-started recently. Mistakes, such as jump-starting the battery with the cables reversed and grounding the alternator’s battery terminal with a wrench, can cause the fuse to blow.

A blown alternator fuse will prevent the charging system from working properly, leading to a variety of problems that can mimic a bad alternator. Before condemning the fuse, however, you’ll want to perform a thorough diagnosis of the vehicle to verify the cause of the concern.
Common symptoms associated with a blown alternator fuse include:
Dead Battery
As was mentioned earlier, the alternator charges the battery while supplying the rest of the car with electricity. If the alternator’s fuse or fusible link is blown, the alternator will not be able to charge the battery. The battery then doesn’t store enough power for starting the car or keeping it running.
Lighting Issues
You may notice the headlights and other lighting start to dim if the alternator fuse is blown, preventing the charging system from working properly.
Warning Lights
The charging system warning light on the dashboard will likely illuminate if the alternator fuse is blown. A blown alternator fuse can also trigger the check engine light and many other dashboard warnings due to system undercharging.
Other Electrical Oddities
Your car contains an array of electronics, all of which rely on charging system voltage. As such, a blown alternator fuse can cause a myriad of transient electrical issues, especially on modern, computer-controlled vehicles.
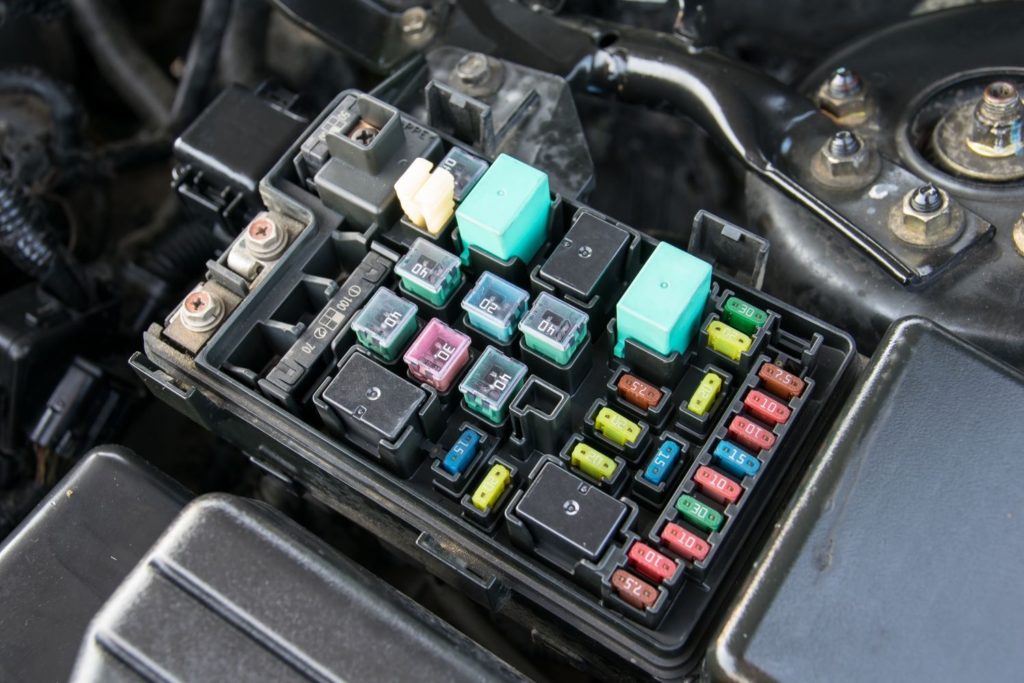

How to Tell if an Alternator Fuse is Blown?
Testing an alternator fuse is no different than testing any other type of fuse. First, perform inspect the fuse by checking whether its conductive element is broken. A broken element means the fuse needs replacement.
If you can’t tell whether the fuse is good just by looking at it, you can use a digital multimeter (DMM) set to ohms to test for continuity. Here’s how to do it:
- Make sure the vehicle’s ignition switch is turned OFF.
- Set your digital multimeter (DMM) to the ohms setting.
- Connect one meter lead to one of the fuse’s terminals. Connect the other meter lead to the other fuse terminal.
- If your meter reads out of limits, the fuse is bad and needs replacement. A reading of anything other than out of limits (OL) indicates the fuse is intact.
The video below demonstrates testing an alternator fuse with a DMM:
How Do You Change an Alternator Fuse?
How you replace an alternator fuse will depend on its type.
- Blade-Style Fuses: Pull them up and of their socket.
- Cartridge-Style Fuses: Pull them up and out of their socket. Some bolt into place, so be careful when removing them.
- Bolt-Dowel Fuses: Use tools to unbolt them.
In some cases, the primary alternator fuse may actually be a fusible link, which must be cut out of the wiring harness to be replaced.
Remember: No matter what kind of fuse you’re dealing with, you’ll want to disconnect and isolate the negative battery cable prior to replacement.
The video below demonstrates replacing one type of cartridge-style fuse:
Alternator Fuse FAQ
Not likely. The fuse serves as a protection device, blowing to keep a circuit overload when there’s too much current flow.
In rare cases, a blown alternator fuse can cause a parasitic drain on the battery when it results in an open circuit.
No, it’s not. You can continue driving while your vehicle has a blown alternator fuse, but that doesn’t mean you can forget about it.
When the alternator fuse blows, it means it prevented a circuit overload that could damage parts and even cause a fire.
With the alternator fuse blown, your circuits won’t have any protection. If another excessive current runs through the connection, it could cause problems for the system.
Replacing an alternator fuse is a DIY-friendly repair that you can usually do yourself. But if you’re unsure what caused the fuse to blow in the first place, you might want to have a professional figure it out.
Alternator fuses generally cost less than $20 for just the part itself. Of course, the exact cost will vary depending on a variety of factors, such as the year, make, and model of your vehicle.
The fuse is usually under the hood on the driver’s side, but it’s exact location varies depending on the vehicle. However, the alternator fuse is typically inside the fuse box under the hood on the driver side.
Consult your owner’s manual to determine the location of the alternator fuse on your car.
Replacing Your Vehicle’s Alternator Fuse
A blown alternator fuse or fusible link can make it difficult to start your vehicle. On the bright side, it shouldn’t be too difficult to get a replacement that fits your vehicle with the help of CarParts.com.
The best part? You don’t even have to leave your home to get a replacement. You can use your mobile phone or computer to visit CarParts.com. Browse our catalog and check for fitment with the help of our vehicle selector. Simply input your vehicle’s details, including its exact year, make, model, and engine.
We only source our parts from the most trusted manufacturers in the industry. It’s also worth mentioning that our warehouses are located all over the US, meaning you can receive your order within days.
Browse our collection of high-quality auto parts at CarParts.com.
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.