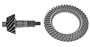The engine, transmission, and wheels are usually the first few things that come to mind when talking about how a vehicle works. And while all of these play a crucial role in your daily driver’s operation, that doesn’t mean that the small parts are not as important.
Spark plugs, bearings, and relays are examples of some of the small car parts that play big roles in the overall operation of your vehicle. But for this article, we’ll be talking about another small yet important part known as the spider gear, which plays an essential role in the differential.
What Is a Spider Gear?
A spider gear is an example of a bevel gear that rotates around the differential case. The spider gears are necessary for the tires to rotate smoothly at various speeds while turning.
Inside the differential case, there are two side gears and two pinion gears. The pinion gears are technically the spider gears, but many people simply refer to all four of the gears as spider gears.
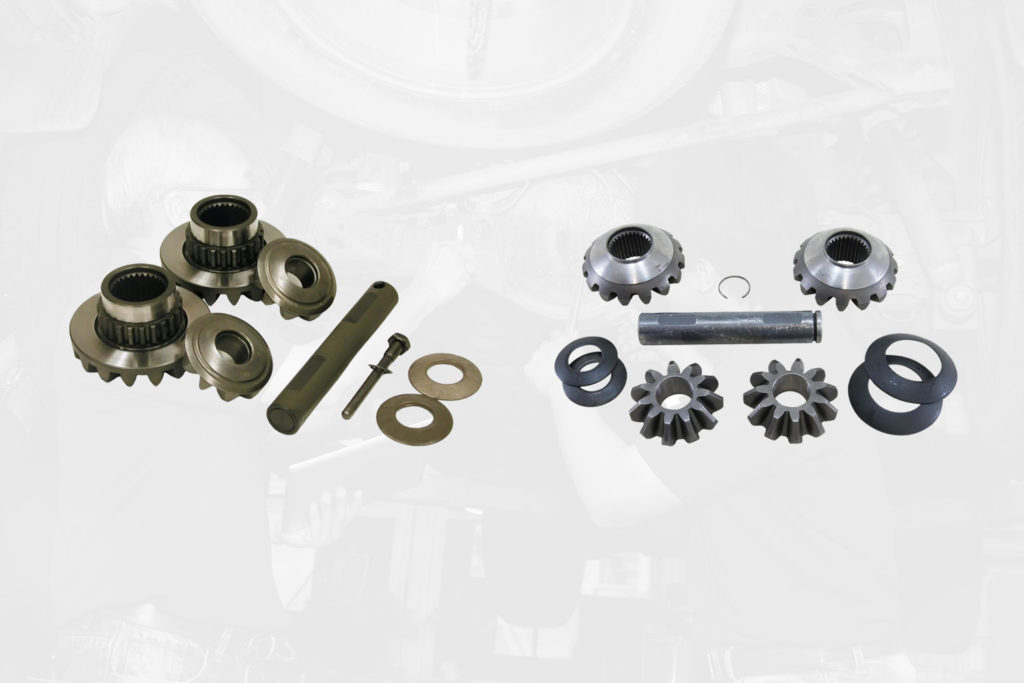

The spider gears take the driveshaft’s rotational energy and channels it towards the axles and on to the tires.
What Is a Standard Differential and How Does It Work?
A differential is an assembly that transmits and distributes the torque from the engine to the wheels. It also makes it possible for the wheels to turn at different speeds while cornering, which prevents one wheel from skidding during the turn.
When the vehicle is driving in a straight line, a ring and pinion gear set turns the differential case. The pinion shaft and spider gears inside of the case drive the side gears and the axle shafts. But as the vehicle turns to a corner, the torque forces cause the side gear and spider gears to subtract torque from one side while adding torque to the opposite side.
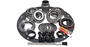
Parts of a Differential
The differential consists of various parts that work together to make the outside wheel travel at a greater distance than the inside wheel. The primary parts include the following:
- Drive pinion gear
- Ring gear
- Differential case
- Spider gears (pinion gears)
- Pinion shaft
- Side gears

Standard Differential vs. Limited Slip Differential
In certain situations, a vehicle equipped with a standard differential does not let the opposite wheel receive enough torque to move the vehicle. On the other hand, in the case of a limited slip differential, torque can be distributed equally or unequally so that the wheels can turn at the same or at different speeds.
How Does a Limited Slip Differential Work?
There are several limited slip differential designs found in different vehicles. However, a typical limited slip differential works by using two mechanisms. First, a coil, Belleville, or leaf spring supplies torque to two side gears. Then, a multi-disc clutch pack sits behind one or both side gears.
How Do Spider Gears Work in a Differential?
As the rear differential case rotates, the cross-shaft applies a drive force to the spider gears, which then causes the two side gears to produce a reaction force to counter the drive force.
The two reaction forces are deemed equal because the spider gear can rotate around the cross-shaft freely.
Once the side gear applies a force to the spider gear, the spider gear applies an equal and opposite force, which then supplies the axle with torque to drive the wheel.
The equal force supplied to each side gear results in an equal torque distribution to each wheel. This is true regardless of whether one wheel is spinning faster than the other or at the same speed.
Keep in mind that the spider gears only rotate whenever the wheel is being turned. Traveling on a straight and smooth path means the ring gear, differential case, and drive axles are moving at the same speed and rotating as a unit.
What Causes Spider Gears to Break?
Free spinning your wheels can cause the spider gears to rotate at an alarming rate and result in metal-to-metal contact.
Once this happens, the cross-shaft and spider gears can melt and damage the entire spider gear and ring and pinion set as well as the differential case.
A worn-out clutch pack can also result in a play in the spider gears, generating a small contact area and causing the spider gears to chip.
Symptoms of a Bad Spider Gear
Grinding or rattling noises when turning are usual indicators of a bad spider gear. In most cases, you won’t hear these sounds when driving in a straight path because the spider gear doesn’t rotate around the differential case during this period.
Keep in mind that a bad spider gear can damage other parts of the differential, which can lead to costly repairs down the road. Make sure to have your vehicle inspected by a certified mechanic at the first sign of trouble.
Spider Gear Replacement

When replacing your vehicle’s damaged or worn-out spider gears, you might need to remove several parts like the tires, brakes, differential cover, clips, axle shafts, and cross pin bolt.
Also, note that it is possible that other parts in the differential system have been affected by the bad spider gear. So make sure to have your vehicle thoroughly inspected for other signs of damage.
In some cases, rolling out the old spider gears is possible to install a set of new ones. However, under extreme circumstances like having pitted gears, mechanics might have to remove the carrier assembly and inspect it for signs of metal contamination in the differential system.
When replacing your spider gears, you’ll most likely have to replace the side gears, too because these gears tend to mesh together and wear out at the same time.
The Bottomline
Like any other car part, spider gears can wear out or get damaged and affect your vehicle’s drivability. If left unaddressed, a faulty spider gear can even affect and damage other parts of the differential.
So, if you need to replace your vehicle’s spider gears, make sure to have a certified mechanic inspect the surrounding parts of your differential as well. This will help you ensure that all parts are operating properly.
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.