There’s a lot of technology millennials and members of Gen-Z missed out on—or were fortunate enough to avoid, depending on how you look at it—ranging from 8-track tapes to typewriters. In the automotive realm, the carburetor is one such long-forgotten technology.
As a millennial myself (albeit an older one), I had never worked on a carburetor until a couple of weeks ago, despite the fact that I’ve been in the automotive industry for 17 years. Like many people from my generation, I avoided carbs at all costs because, well, to be honest, I couldn’t tell a main jet from a float valve.
But alas, I couldn’t escape carbs forever. The motorcycle I bought a few years ago recently became hard to start and would intermittently stall, so I knew it was time to give the carbs a rebuild. I also added a K&N air filter and installed a jet kit while I was at it.
To my surprise, the project actually turned out to be a lot of fun. I would like to share with you what I learned along the way as a carburetor newbie.
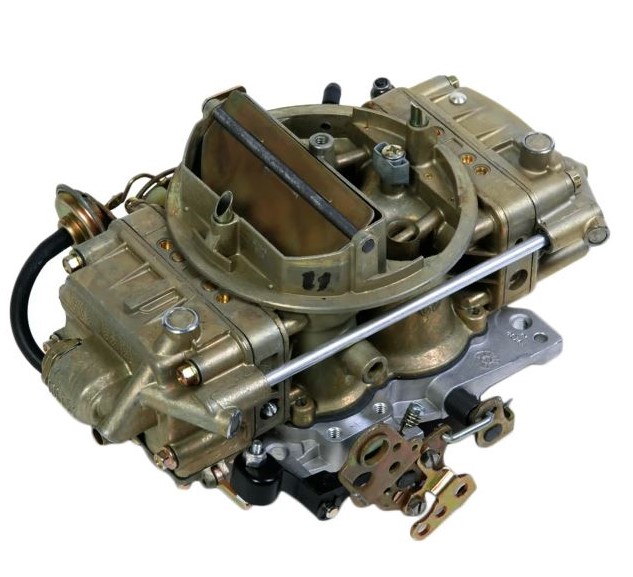

What Does a Carburetor do?
If you’re under the age of 40, there’s a good chance the only time you’ve encountered a carburetor is while mowing the lawn. Although carburetors haven’t been used in production automobiles in about 30 years, you’ll still find them in lawn mowers, snowblowers, and other machines with small engines. Some older motorcycles, like mine, also have carbs.
Like the fuel injection systems found on modern vehicles, carburetors are designed to deliver a metered amount of fuel into the engine. Of course, a carb is a mechanical device (except some have an electric choke), whereas the fuel injectors on modern engines are computer-controlled.
How Does a Carburetor Work?
Even though there aren’t many vehicles with a carb under the hood anymore, it’s helpful to know how the technology works. You never know when you might end up tinkering with a classic car, a snowblower, or (in my case) a motorcycle.
So, how does a carb work? It all starts with the engine’s intake stroke, in which a piston moves downward inside the engine, creating a vacuum, and pulling air past the choke valve (more on that later) and into the barrel of the carburetor.
Next, the air moves through the narrow portion of the carburetor called the venturi. The venturi creates a low-pressure condition that pulls fuel from the carburetor’s fuel bowl (the bowl contains a float and valve to prevent over-fueling). Then the fuel gets siphoned into a jet, which meters fuel into the carburetor. From there, air and fuel mix and enter the engine through a throttle plate.
Some carbs have only one fuel metering circuit and jet, while others have multiple jets to supply the right amount of fuel across a broad operating range. Most carburetors also have an accelerator pump circuit that squirts extra fuel into the carb under heavy acceleration.
Also, carburetors generally have a choke (as we mentioned earlier), which is a throttle valve that’s opened to enrich the air-fuel mixture when the engine is cold.
It’s worth pointing out that the description above explains the interworkings of a single-barrel carburetor, but many automotive carbs have multiple barrels.
The video below demonstrates how a single-barrel carburetor (with only one fuel circuit and jet) typically works on a lawn mower.
What I learned While Rebuilding My Carburetor
The main thing I learned from rebuilding my carbs is that the technology isn’t as intimidating as those of us who grew up with fuel injection might believe. Even though the single-barrel carbs on my motorcycle aren’t nearly as complex as some of the multi-barrel units on a car, the underlying principles are the same.
Don’t be afraid, fellow millennials. If you’re a DIYer with a carburetor that’s in need of repair, I encourage you to tackle fixing or rebuilding it yourself. Just keep everything clean and organized while paying attention to where all of the parts go, and you’ll be fine.
While rebuilding my carburetors, I used a Haynes repair manual as my primary guide, supplemented by YouTube videos. If you’re embarking on your first adventure with carbs, as I did, I highly recommend having a repair manual on hand instead of relying solely on YouTube videos.
Another thing to keep in mind is that everything is mechanical, which means there’s quite a bit of fine-tuning to be done after the rebuild. On my motorcycle, it’s suggested that you adjust the engine’s valves before syncing the carburetors and performing the idle and mixture adjustments.
There’s no computer to adjust the air-fuel mixture and make life easy—you need to use a screwdriver to take matters into your own hands.
Why I Still Prefer Fuel Injection
At the end of the day, I still prefer fuel injection over carburetors, despite my successful rebuilding endeavor. With today’s fuel injection systems, there’s no need to perform precision adjustments to get the engine running right. Plus, in almost any situation, a fuel-injected engine will fire right up without the need for a choke or pumping the gas pedal.

While I’m glad I learned about carbs while rebuilding the set on my motorcycle, I plan on purchasing a fuel-injected bike next time. But the good news is, I’m now prepared to deal with the carburetor on my lawn mower the next time it starts acting up—and that’s a good thing.
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.