The camshaft on many engines includes both intake and exhaust valve lobes. In other words, the intake and exhaust camshafts are all part of the same component.
But on dual overhead cam engines, the exhaust camshaft will be a separate shaft, and it basically does the same thing the intake camshaft does; it just opens different valves.
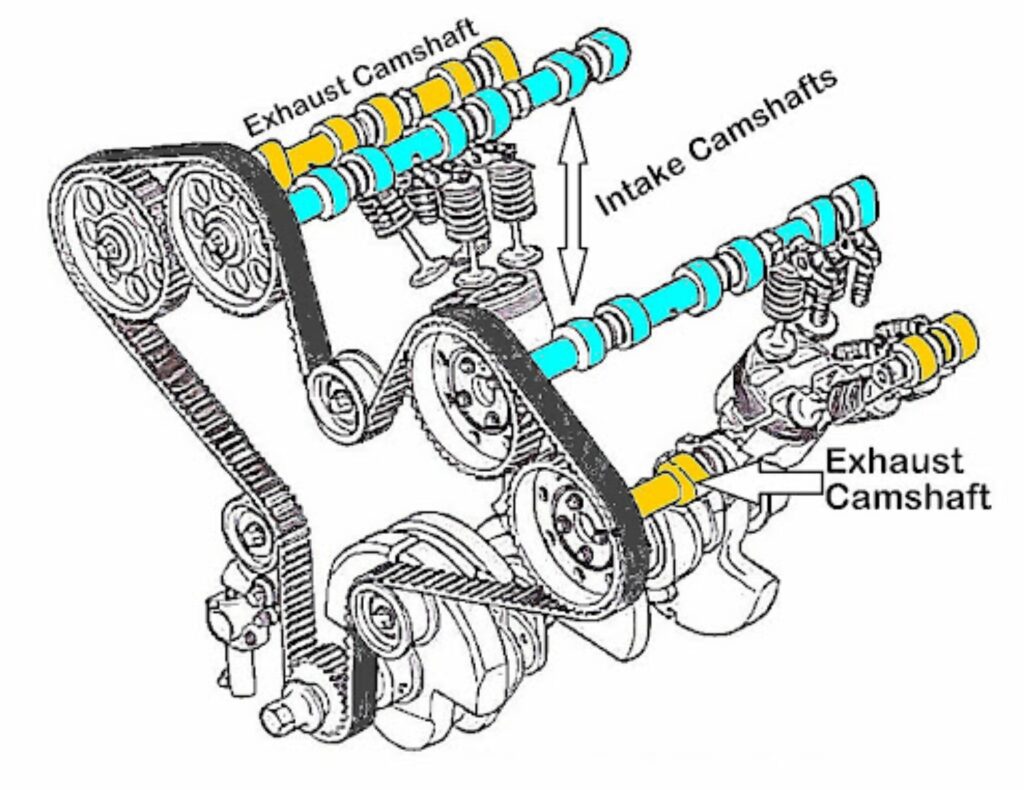
Exhaust cams are responsible for how long the exhaust valves remain open and how much they open. “Lift” describes the amount of opening and “duration” describes the amount of time they’re open. Both depend on the shape of the lobe operating the valve. The shaft has to be perfectly in time with the crankshaft and the other camshaft.
When Should You Replace an Exhaust Cam?
Popping Noises in the Exhaust
If you hear popping noises in the intake manifold, they may indicate induction backfire. This occurs when there are issues with the ignition system, including but not limited to faulty spark plugs, cross-firing between distributor posts, and timing errors. Eliminate all these other things before suspecting the exhaust camshaft.
Engine Misfiringthe old
While misfires are a common concern, they’re almost never caused by either of the camshafts, although they can be the cause of a misfire or lost power if a lobe is worn enough to affect valve operation.
If a bad exhaust cam is responsible for a misfiring engine, it’s important to have it replaced right away once you have verified that’s the problem.
How to Remove an Exhaust Cam
Bear in mind that tampering with the engine without intimate knowledge of the various components and what they do is a recipe for disaster. It’s better to hire a mechanic to diagnose and replace your exhaust cam if needed.
Here’s an overview of what the process of removing an exhaust cam might involve:
- The camshaft can be removed without removing the timing cover, which is often the case on 4-cylinder engines with overhead cams. But the timing chain and gear must be detached from the camshaft before it can be removed. This can be done by just removing the rocker arm cover.
- The valve covers are lifted so that the Mass Air Flow and Intake Air Temperature sensor assembly can be removed.
- Spark plug wires and wiring harnesses connected to the coil packs are removed from the valve covers.
- The mechanic accesses the crankshaft and turns the camshaft wheel to align the timing marks. The wheel is turned until the V-shaped timing mark is at the top.
- The old camshaft is removed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about exhaust cams.
What are exhaust cam sensors for?
Exhaust cam sensors provide cam sensor position to the ECM/PCM for injector and valve timing.
What are exhaust cam actuators for?
The exhaust cam actuator is the device that advances or retards exhaust valve timing for emission control and efficiency, but not all vehicles have this. Some just have fixed valve timing.
What is the difference between an intake cam and an exhaust cam?
The intake cam, or the intake camshaft is responsible for controlling the intake valves in the engine. It opens the intake valves at the perfect time, allowing the air-fuel mixture to enter the combustion chamber. This affects a vehicle’s power output, torque, and fuel efficiency.
On the other hand, the exhaust cam is responsible for controlling the exhaust valves in the engine. It opens the exhaust valves so that exhaust gases can exit the combustion chamber. The exhaust cam determines the timing and duration of the exhaust opening, affecting the engine’s performance and emission levels.
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.