Modern vehicles are equipped with different sensors that ensure engines run as they should. Oxygen (O2) sensors, for example, measure the oxygen content in the exhaust. They come in two variants: upstream and downstream O2 sensors.
What’s the Difference Between an Upstream and a Downstream O2 Sensor?
Upstream and downstream oxygen sensors play crucial roles in ensuring optimal engine operation. They differ in terms of their location and function.
Location
Both oxygen sensors do not always connect to the catalytic converter. The upstream oxygen sensor can be found either before the catalytic converter or at the front. Meanwhile, a downstream oxygen sensor is located after or at the end of the catalytic converter.

Function
Upstream O2 sensors are high-authority sensors that help with the vehicle’s fuel trim. The fuel trim refers to the adjustments that the powertrain control module (PCM) make to maintain the correct air-to-fuel ratio in the engine.
An upstream O2 sensor detects oxygen content so that the computer can adjust the fuel injector pulse width to improve fuel economy and ensure that the engine runs properly.
Meanwhile, downstream O2 sensors monitor oxygen content just like the upstream sensors. Additionally, a downstream sensor is also used to measure the efficiency of your catalytic converter.
The catalytic converter turns harmful exhaust gases “safer,” so the gases entering it must leave with little to no pollutants. In short, the upstream O2 sensor must detect more pollutants than its downstream counterpart.
Are Upstream and Downstream O2 Sensors Interchangeable?
No, you can’t because they serve different purposes and have different connection spots.
How to Tell Which O2 Sensor Is Bad
Both O2 sensors will illuminate the check engine light when they’re faulty because they can cause performance issues and damage the catalytic converter.
On-board diagnostics will log a trouble code to indicate the problem, and you can use a scan tool to retrieve it. The code can help you identify which oxygen sensor is faulty. However, take note that a code would not automatically mean that a sensor is faulty. Problems in internal wirings, engine issues, and ignition system faults can also trigger the same trouble code. Issues with the fuel system can also be the culprit. Do not replace any faulty part based on a code alone.
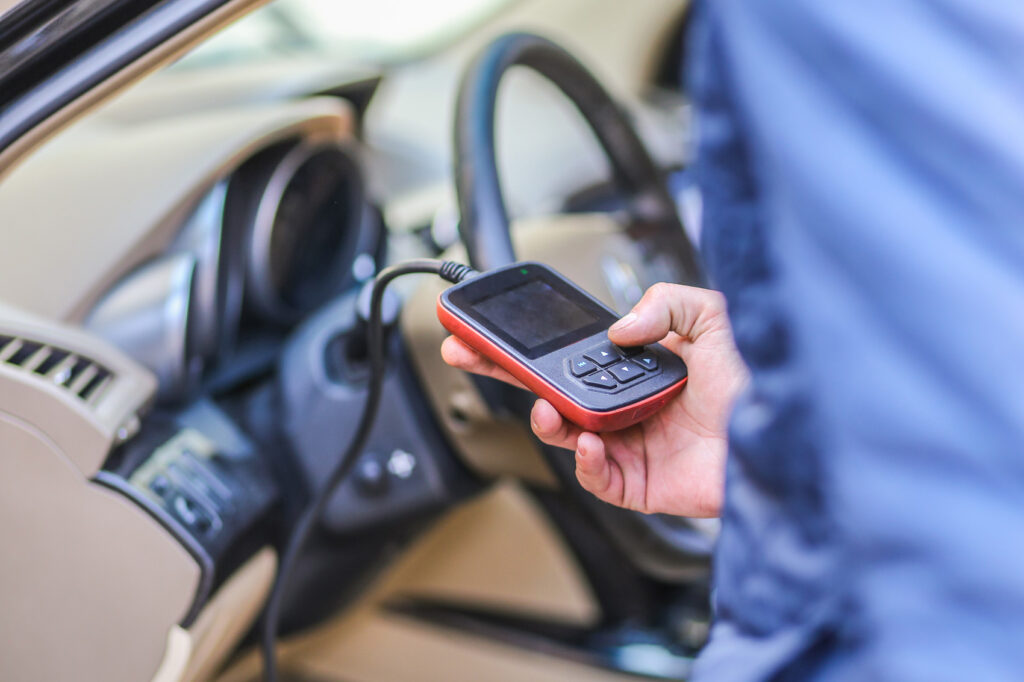

For example, if your scan tool retrieved a P0142 code, it means that the issue is with the O2 sensor circuit in Bank 1 (Sensor 3). That refers to the third sensor downstream from the engine.
Aside from relying on a scan tool, you can use a digital voltmeter to test your O2 sensors. It can help you determine whether they’re still giving accurate readings. If you’re not familiar with how vehicles work, it’s best to let a mechanic test the oxygen sensor. The sensor’s readings can be tricky to interpret without the right tools and engine data.
If you’re not familiar with how vehicles work, it’s best to let a mechanic test the oxygen sensor. The sensor’s readings can be tricky to interpret without the right tools and engine data.
–Anthony Harlin, ASE Certified Master Automobile Technician
Air Fuel Sensors
In newer vehicles, the upstream oxygen sensor is often referred to as an air fuel sensor, and it operates on amperage instead of voltage. Unlike a traditional oxygen sensor, testing an air fuel sensor with a voltmeter is not suitable. If you’re replacing an oxygen sensor, make sure that you know if your vehicle is using an air fuel sensor or an oxygen sensor.
How Many Oxygen Sensors Do Vehicles Have?
Most cars have at least two. The number depends on the vehicle’s year, make, and model. Engine size can also play a factor. Generally, here’s an oxygen sensor after your catalytic converter. If your car has a v6 engine, it’s supposed to have two catalytic converters and two downstream sensors. In most v style engines (v6, v8, v10), there’s one upstream sensor per bank. In some cases, however, there will only be one upstream sensor. However, this setup is rare. You can check your owner’s manual to determine how many sensors your vehicle has.
You can also check this video to get an idea of how oxygen sensors work:
Causes of O2 Sensor Failure
There are many factors that can affect the lifespan of O2 sensors. Let’s look at each of them in detail.
Extreme Wear From Age
It’s normal for O2 sensors to age as your car gains mileage. A typical O2 sensor can last around 30,000 to 50,000 miles. However, that’s not always the case, as it can develop issues over time.
Electrical Issues
O2 sensors have circuits, so they can have electrical problems. If the heater circuit, for example, malfunctions, the O2 sensor might not work at all.
Damage and Contamination
Water and road salt can damage O2 sensors. The O2 sensor’s zirconia cell is also sensitive to contamination. Oil ash and coolant contamination can make them malfunction and provide inaccurate readings, leading to poor performance and decreased fuel economy.
Can You Drive With a Bad O2 Sensor?
Yes, you can drive while your vehicle has a faulty O2 sensor, but that doesn’t mean you should. Bad O2 sensors can cause performance issues because they affect other car parts.

For example, when the O2 sensor is faulty, the powertrain isn’t operating on the right amount of air and fuel. This can cause your catalytic converter to fail over time.
How Much Does It Cost to Replace an Oxygen Sensor?
An aftermarket O2 sensor can cost you anywhere between $20 and $100, depending on the brand, type, and specs. You’ll also have to consider labor costs if you’re not DIY-ing the replacement.
Should I Replace All O2 Sensors When One Is Bad?
Experts recommend replacing your O2 sensors in pairs to ensure their consistent operation. For example, if your left upstream sensor is bad, it’s best to also replace the right one.
Replacing an Oxygen Sensor
Replacing your O2 sensor isn’t that complicated. If you’re well-versed in auto repair, you can do the procedure on your own. However, make sure you follow replacement instructions that are specific to your vehicle’s year, make, and model.
If you’re in doubt about anything, you can always ask a mechanic to replace the faulty O2 sensor. Leave the task to an ASE-certified mechanic to ensure your vehicle is in good hands.
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.





























I ordered a set of 02 sensors for 04′ dodge durango and they came as a pair A2 2of them and a pair of B2. 2 if them a d each of them (all 4) say 1,2,3,4 on the sensors. What are the chances of them working since all say 1234. As Long as A2 on sane side and B2 on other side will they still work.