Gear ratios impact your vehicle in interesting ways. Manufacturers are always on the lookout for the perfect blend of performance and fuel economy in every vehicle they release, and figuring out the right gear ratio is a big part of the process. Today, we’ll be delving into what gear ratios are and how they affect your everyday drive.
Gear Ratio Basics
First things first, let’s understand what gear ratio is in the first place. To put it simply, the gear ratio indicates how two or more interlocking gears relate to one another. In this case, these two gears are called the drive gear, also known as the driving gear, and the driven gear. The torque is applied to the drive gear in order to rotate the driven gear in turn. Gear ratios are typically utilized in vehicle transmissions in order to manipulate torque. Lower gears multiply torque at the cost of engine rpm, and higher gears sacrifice torque in favor of faster top speeds.
Typically depicted using the ratio formula (x:y), gear ratios indicate both the size of the gears relative to one another and the number of rotations they turn when connected to one another. For instance, if a bigger gear is connected to a smaller gear and is twice as large as the smaller gear, their gear ratio will be depicted as 2:1 (two to one). This also means that for every one rotation of the larger gear, the smaller gear will rotate twice. Gear ratios are used to multiply or divide torque.
The ratio can be found using the gears’ teeth as well. The number of teeth can indicate the ratio once they’ve been reduced to their smallest fraction equivalent. For instance, if one gear in a gear pair has 20 teeth and the other has 40, the gear ratio would be 40:20, or the same 2:1 as in our original example. Automakers use gear ratios to create gear trains, which determine how the torque gets transmitted to the wheels.
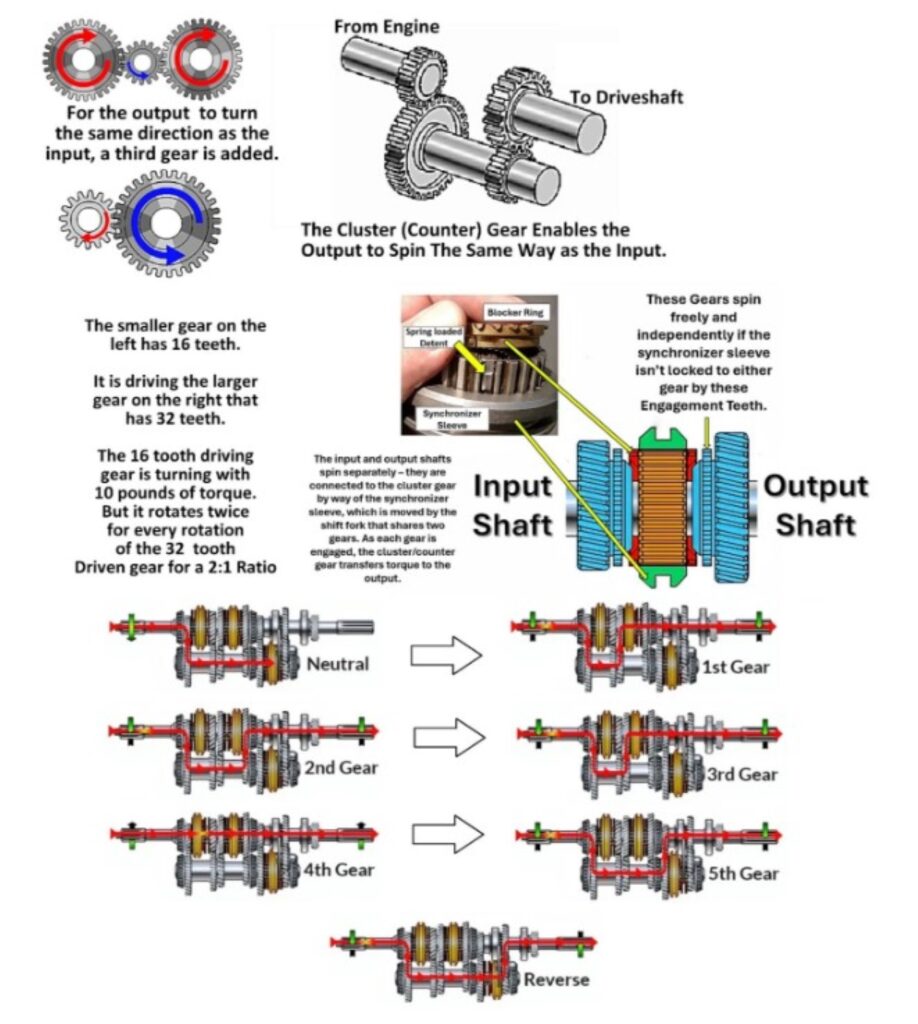
What Are Transmission Gear Ratios?
To fully understand how gear ratios affect your vehicle, we need to take a closer look at the different types of gear ratios being used and what they do, starting with transmission gear ratios.
Transmission Gear Sets
When your engine fires its spark plugs, the fuel inside the combustion chambers ignites, pushing the pistons. These pistons move up and down in a pattern, rotating the crankshaft that they’re all attached to. The crankshaft in turn is connected to the transmission through a set of gears. The gears attached to the crankshaft are the drive gears and those that attach to the output shaft, which lead to the wheels, are the driven gears. Each set of gears has a different gear ratio, and only one set is engaged at a time, allowing for the torque from the engine to be transmitted to the wheels for different purposes. The shifter allows you to switch between these sets.
Gear Ratio Purposes
On lower gears, the drive gear has to rotate more times in order to make the driven gear rotate once. As an example, let’s say on lower gears, the gear ratio is 3:1. In this instance, for every three rotations of the drive gear, the driven gear rotates once. Using this gear ratio, a high amount of torque gets transmitted from the engine to the wheels in exchange for a slower speed.
On higher gears, the driven gears get smaller and closer to the drive gear in size. This change results in a gear ratio that’s closer to 1:1. For our example, let’s say the higher gear set has a gear ratio of 1.5:1. This means that for every rotation of the driven gear, the drive gear needs to rotate one and a half times to turn it. The smaller the driven gear is, though, the more torque it needs for it to rotate. This results in a higher top speed but with much less torque.

How Do Gear Ratios Affect Mileage and Acceleration?
Gear ratios affect both your vehicle’s mileage and acceleration. Lower gear ratios, which are associated with higher gears, result in slower acceleration but better fuel economy. The opposite is true for higher gear ratios associated with lower gears. That’s why vehicles have different gear ratios in the first place, to allow the driver to adjust to what they need on each type of road.
Gear ratios can be rather challenging to understand at first, but they’re integral to how your transmission functions. The way they affect mileage, acceleration, and torque makes them a worthwhile subject to study. At least now you’ve got a head start on the basics.
Getting Your Hands on New Transmission Parts
Don’t hold off on replacing faulty or inoperative transmission parts as soon as your mechanic recommends it. Shop online, and grab the best deals today at CarParts.com.
A team of industry professionals handpicks and vets all products in our catalog. These parts are sourced from today’s top brands and are manufactured in world-class facilities using the most advanced technologies. The best part? We buy them in bulk and pass on the savings to you.
Start shopping by downloading our mobile app or visiting our website. Use our vehicle selector to check for fitment, and toggle our search filters to shop by brand or price range. This way, you can easily find auto parts designed to work with your vehicle.
Need parts for urgent repairs? Orders are shipped from strategically located distribution centers to guarantee that your orders arrive in as fast as two business days.
Shop and order today!
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.