Your vehicle’s A/C compressor is an important part of its A/C system. An inoperative A/C compressor can cause issues with the A/C itself. No one likes sitting in a hot vehicle cabin in the summer, so it’s best to have a mechanic fix your vehicle’s faulty A/C compressor as soon as possible.
Due to this project’s complexity, we don’t recommend performing these repairs yourself. In this article, we’ll go over some tips for replacing a bad A/C compressor, so in case you decide to watch your mechanic repair the faulty part, you at least know what’s going on.
What Is an A/C Compressor?
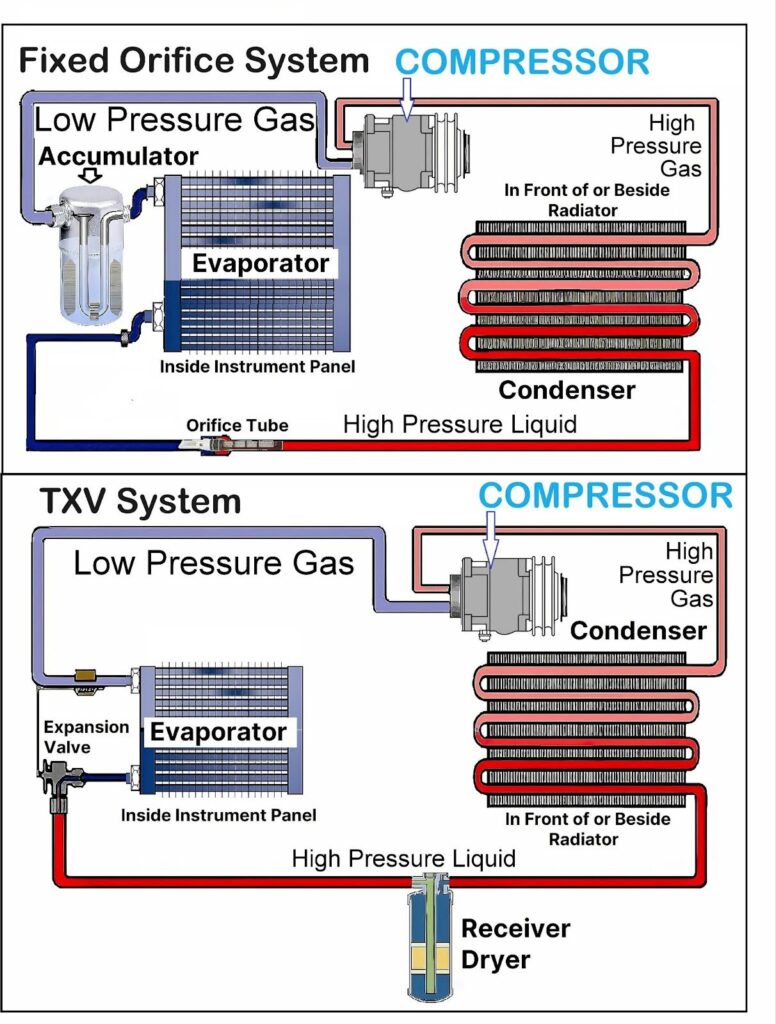
In modern vehicles that aren’t hybrid or EV, a serpentine belt drives the A/C compressor, which in turn circulates the A/C system’s refrigerant.
The compressor squeezes refrigerant vapor into a high pressure vapor, sends it through the condenser, where it changes to a liquid, giving up heat in the process.
The liquid refrigerant then travels through an orifice (either fixed or variable), which restricts the flow of liquid refrigerant so that it enters the evaporator as a low pressure liquid that changes from a liquid to a gas, absorbing heat and de-humidifying the air that passes through it and into the vehicle cabin.
Faulty A/C Compressor Symptoms
If your vehicle exhibits the following symptoms, take it to an automotive repair shop:
- Inoperative A/C
- Damaged or screeching drive belt
- Abnormal noises when using the A/C
Tips for How To Replace an A/C Compressor
Here are some things professionals use for A/C compressor replacement:
Caution: Deliberately releasing refrigerant into the air is illegal. A machine must be used to remove refrigerant from the system before disconnecting refrigerant lines. With direct contact to the air, liquid refrigerant that makes contact with your eyes can cause blindness and can cause frost-burns on your skin.
Tools
Professional mechanics know that scrambling for tools in the middle of a project will hinder their work. Here are some of the items you might see them use:
- A new A/C compressor
- Wrench and socket sets
- Replacement refrigerant
- New hoses, gauges, and thermometers
- Serpentine belt tensioner
Process
While replacing your faulty A/C compressor, a good mechanic will remember to check the refrigerant lines for damage and greasy spots that indicate a leak. Any leaking lines need to be replaced.
After the components have been replaced and the system is sealed (fittings tight, etc.),the atmosphere within the sealed system must be pumped out using a vacuum pump. There are several types of vacuum pumps, and unless you’re a very serious DIY person you probably don’t have one.
The atmosphere must be removed because air doesn’t condense into liquid like refrigerant does (with a lot of air in the system you’ll find yourself with an air compressor); the pressure in the system will rise to dangerous levels.
When the system has been evacuated with the vacuum pump, the mechanic will put the right amount of the right kind of good refrigerant, and the right kind of refrigerant oil into the system. Compressors come with oil, but accumulators, evaporators, and condensers don’t. Oil must be added if these components are replaced.
The oil flows through the system mixed with the refrigerant, lubricating the compressor. Having too much oil will prevent the system from cooling properly because it coats the inside of the evaporator and condenser. Not enough oil and the compressor will very soon be destroyed from lack of lubrication.
After the system is charged, high and low side pressures are monitored along with the temperature of the air coming through the register inside the vehicle cabin while the engine is held at about 1500 rpm.
The operation of the radiator fan is evaluated as well. If the radiator fan isn’t working, either sometimes or all the time, the condenser will only be able to convert the refrigerant to liquid when the vehicle is moving. The A/C may not work when sitting still if the fan doesn’t move air through the condenser.
Common Issues to Check Before Compressor Replacement
Before deciding to replace a compressor that doesn’t engage, a good mechanic will check the electrical side of the system (the switches, relays, wiring, etc.). Throwing a compressor at a non-functional A/C before checking everything else is unwise.
Here are some common issues to check before compressor replacement:
Faulty Electrical Components
If no power is reaching the compressor, it’s possible that faulty wiring, relay, or fuses are to blame. A good mechanic can inspect the electrical components for issues and replace any inoperative parts.
Compressor Not Cooling
If the compressor is engaged but there is no cool air at the register inside, the temperature of the suction line (the large one that comes from the evaporator) should be checked. This line should be frosty cold all the way to the compressor when the system is engaged. The discharge line leaving the compressor and the liquid line leaving the condenser should be hot. If not, the pressures will tell the tale.
If the suction line is cold and the discharge and liquid lines are hot but there is no cold air, the heater blend door may be allowing warm air to mix with the cold air. If the evaporator freezes up and blocks airflow because the compressor never cycles off, there may be a stuck relay or pressure switch.
A healthy system on a hot day should have a low side pressure of between 30 and 50 degrees F, and a high side pressure of from 175-300 F. The temperature/pressure of the two sides is greatly affected by ambient temperature.
But if the A/C isn’t cooling and the low side pressure is higher than it should be and the high side pressure is lower than it should be on a fully charged system, the compressor is worn out and needs to be replaced.
If both sides are low on a fully charged system, the orifice tube or Expansion Valve (TXV) is usually at fault.
Refrigerant Leaks

Compressor Clutch Not Engaging
Your mechanic will check any wiring and fuses linked to the system. If those are fine, they might need to replace the clutch.
Noises From the Compressor
If you hear any unusual noises when the compressor is engaged, it can mean the compressor is beginning to fail, or in some cases (very rare), it might be due to loose mounting bolts.
It’s always safest to hire a professional mechanic to replace your A/C compressor. It’s a complex job that requires machinery you won’t find or need in an average garage. Still, it’s good to keep these handy tips in mind when choosing a mechanic or auto shop to take on the project. Now you know what they need to do to repair your vehicle’s faulty compressor and some of the things you can do to make the process easier.
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.