Do you need to get more performance out of your car? Installing a supercharger is one of the simplest and most popular approaches to increase engine power. Car manufacturers even install them as standard-issue equipment in some vehicles to help smaller engines match the output of bigger power plants without producing higher emission levels.
But what is a car supercharger, exactly? What does it do, and how does it work? Are there more than one type of supercharger, and how do they differ?
What Is a Supercharger?
Superchargers and are basically air pumps designed to compress air and force it into the intake under pressure.
You may think superchargers only appear in high-performance cars. After all, engine power is critical to vehicles like drag racing cars that require high speeds and lightning-fast acceleration. Indeed, superchargers give drag racers the extra power they need to eke out narrow wins on the highly competitive track.
Thus, you might find it surprising to find superchargers in some street-legal vehicles like the Chevrolet Cobalt SS, Mercedes-Benz CLK 200K, and Toyota MR2. These models have engines with smaller displacements that release fewer tailpipe gasses at the cost of producing less power and torque. A supercharger enables their engines to produce enough horsepower and torque while remaining in compliance with emissions standards.
How Does a Supercharger Work?
The supercharger boosts the charge air pressure in the engine. Most superchargers have a compressor or a similar component that compresses the air intended for the engine. Compressed air improves the combustion process, generating more power and torque.
An internal combustion engine (ICE) is basically a breathing machine that captures atmosphere, adds atomized fuel, compresses that mix above moving pistons, then creates a carefully timed ignition event in each cylinder right before the piston reaches the top of its travel.
Engine design has a lot to do with how well the fire-breathing powerplant under your hood captures air. While the atmosphere weighs 14.7 pounds per square inch (1 bar) at sea level, the downward movement of each piston on its intake stroke creates low pressure that the atmosphere naturally rushes in to fill.
Engine design has a lot to do with how well the fire-breathing powerplant under your hood captures air.
– Richard McCuistian, ASE Certified Master Automobile Technician
Air has to make its way through the filter, the air inlet tube, past the throttle plate to pressurize the plenum chamber on its way into each cylinder. Because of all these hurdles and their stacked resistance to flow, a naturally aspirated 3.0 liter engine may only get 2.0 liters of air during each full cycle.
Forcing the air into the cylinders helps increase volumetric efficiency, and that’s what superchargers and turbochargers are for.
What is the Difference Between a Turbocharger and a Supercharger?
A turbocharger has a turbine driven by the exhaust stream connected to an impeller in the intake stream, can spin up to over 100,000 rpm, and is oiled by the engine’s existing pressurized lubrication system.
A supercharger is mechanically driven by gears or a belt connected to the crankshaft and usually has its own discrete oil supply that doesn’t mix with the engine oil.
While a supercharger robs a bit of power from the engine, it enables the engine to produce a whole lot more power than a naturally aspirated engine. Forced induction engines always have safeguards (wastegates or supercharger bypass devices) to prevent the engine from being destroyed by too much boost.
However, Superchargers have a few advantages over simple turbochargers.
Instant Power Generation
A supercharger responds much faster than a simple turbocharger because the supercharger is driven mechanically rather than depending on the flow of exhaust gas to act on the turbine the way a turbocharger does.
A simple turbocharger has a brief moment of what is called “turbo lag” before air compression begins. When you apply throttle on a Supercharged engine, the supercharger responds instantaneously.
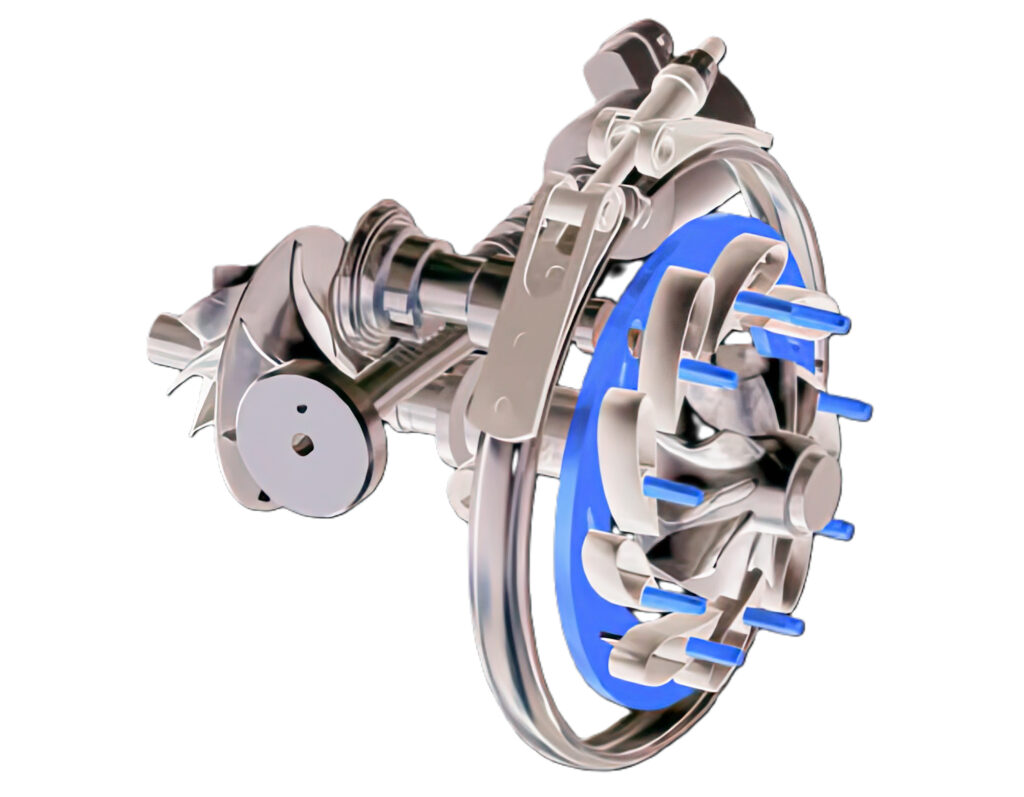

Torque Boost
Superchargers increase torque output across the engine’s RPM range. Your car needs torque to build up speed quickly once you hit the gas. High torque production lets you accelerate faster, contributing to a more energetic driving experience.
Race cars aren’t the only vehicles that can benefit from the extra torque produced by the supercharger. A supercharged car can overtake other vehicles on the highway more easily. Good acceleration can also help you maneuver through traffic on urban roads.
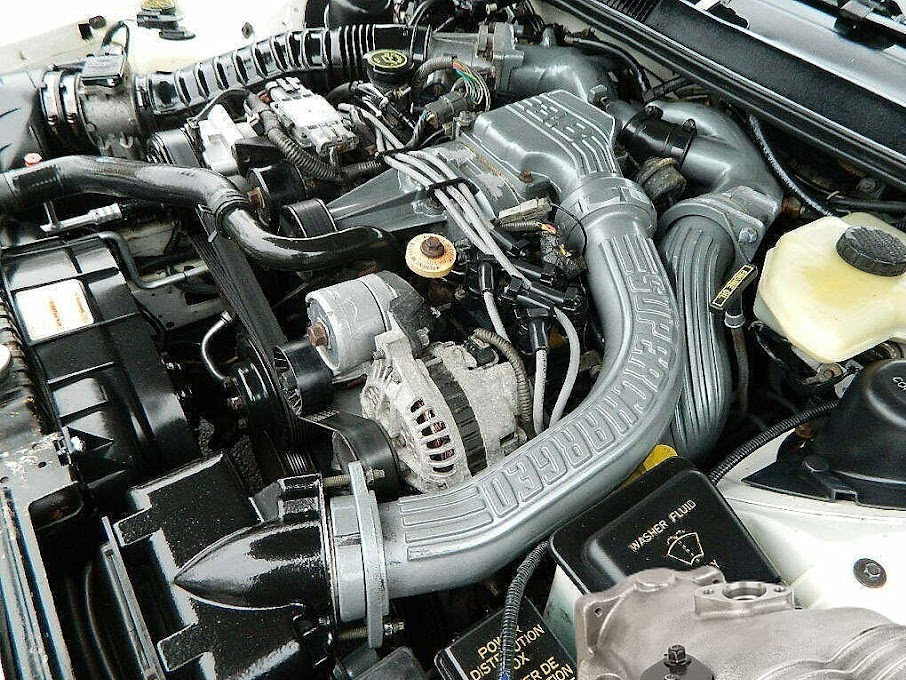


Types of Superchargers
Superchargers aren’t new technology. First introduced in 1878, they started being more widely used in cars in the 1920s. They underwent refinement over the decades to improve their performance.
Several types of superchargers are available on the market. Each type uses a different method of compressing air, leading to differences in performance. Look for the type of supercharger that meets your specific needs.
In alphabetical order, here are the common types of superchargers:
Centrifugal Superchargers
The centrifugal supercharger operates on the same principles as a turbocharger. It relies on an impeller to pull air from outside the vehicle. The impeller also compresses the air before forcing the latter into the engine. But since the supercharger is capturing the atmosphere and forcing it into the engine’s intake system, the engine doesn’t have to depend on its own vacuum. The intake manifold is actually under pressure rather than having a vacuum.
Centrifugal superchargers achieve their best performance at higher engine speeds. They excel at delivering a linear power curve.
Furthermore, centrifugal superchargers are versatile. You can tune these superchargers to deliver the precise power gain you desire.
Roots Superchargers
The roots supercharger features two lobes that look like a set of gears. When the lobes rotate, they mesh together to compress and move air into the engine. They also produce an unmistakable whining sound.
Roots superchargers shine at low engine speeds. They deliver the power boost instantly, letting drivers get more acceleration.
You can usually find roots superchargers in drag racers and muscle cars. Drivers welcome the power boost and distinct whine made by this type.
Twin-Screw Superchargers
A twin-screw supercharger compresses air with two intermeshing rotors. It occupies a sweet spot between instantly delivering low-end power and hitting high-performance levels. Many drivers pick a twin-screw supercharger because their efficient performance and power delivery give the best of both worlds.

Installing and Maintaining the Supercharger
Like other car parts, the supercharger can wear out after several years, especially if it sees heavy use. Whether your car came with a factory-issued supercharger or received one as an upgrade later, you’ll have to replace the part once it becomes too worn or stops working.
In many cases, you can replace the old supercharger if you have enough experience in DIY car repairs. However, you must exert care during the installation process. Otherwise, you might cause a leak that can reduce the engine’s power and torque output. Leaks can also lead to more severe issues that might damage or destroy the engine.
If you’re concerned about your ability to replace the faulty supercharger, you can get a trained mechanic to perform the repair job for you.
Regular Maintenance
No matter the type, superchargers need periodic maintenance if you wish to keep them running. Inspect the supercharger for leaks, change the oil, and check the drive belt.
Engine Tuning
To maximize the power and torque boost of the supercharger, you must tune the supercharged engine. Tuning helps your car run smoothly. If the supercharger isn’t originally part of the engine, tuning also reduces the risk of issues caused by boosting engine power beyond the limits set by the manufacturer.
Quality Parts
You get the performance you pay for. Always use high-quality superchargers and related accessories. Quality parts deliver better performance and enjoy higher reliability.
How Much Does a Supercharger Kit Cost?
A supercharger kit contains various parts and components for repairing a faulty supercharger. If you plan to get one, prepare to shell out between $440 and $850.
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.