Dedicated car owners will go to great lengths to make sure that their vehicles will run for a long time without fail. Aside from keeping up with routine maintenance, they’ll also use recommended products to protect crucial components.
One of these products is anti-seize grease, which is used on several parts, including the spark plug.
What Is Anti-Seize for Spark Plugs?
Anti-seize is a kind of lubricant for various components like spark plugs, bolts, and flanges. It prevents rust, corrosion, and galling from forming on the threads.
The lubricant can come in the form of grease, paste, or coat. It’s usually made from a combination of nickel, copper, inorganic salts, and petroleum oils, among others.
Anti-seize lubricant is applied to parts that are always exposed to high temperatures to reduce premature wear.
For threaded components, applying anti-seize compounds can make their disassembly quick and easy. The compounds can also protect them from acids, ammonia, acetylene, and other corrosive compounds.
Types of Anti-Seize Lubricants
There are various types of anti-seize compounds, like copper and nickel anti-seize. Each variant combines different additives to fit a specific application.

Copper Anti-Seize
A copper-based anti-seize lubricant usually has rust and corrosion inhibitors and antioxidants. It’s highly resistant to saltwater and galvanic corrosion.
Copper-based anti-seize is made from pure copper and large flake graphite, and it can make parts resistant to temperatures as high as 1,800 degrees Fahrenheit. Copper anti-seize also has electrical conductivity properties.
This copper-based lubricant is usually applied to parts like brake caliper bleed plugs, pipeline fasteners, wenches, and more.
Most copper anti-seize products are deemed safe for sensors. O2 and exhaust sensors are usually pre-treated with copper anti-seize on the threads or tubes.
Nickel Anti-Seize
Nickel-based anti-seize is extremely resistant to acidic, caustic, and corrosive environments. It’s ideal for all kinds of threaded fasteners, including stainless steel and aluminum threads.
Nickel-based anti-seize generally works well under temperatures that go as high as 2,200 degrees Fahrenheit.
This type of lubricant has a lesser coefficient of friction than copper-based anti-seize. That means that, while it has better oxidation stability than a copper-based lubricant, it doesn’t work as well in moist environments due to its low water resistance capacity.
Should You Put Anti-Seize on Spark Plugs?
The safe answer is “no,” especially if you have pre-treated spark plugs.
Some spark plug manufacturers advise against using anti-seize because they produce pre-treated spark plugs. That means they’ve already been doused in anti-seize properties.
Doubling the amount of anti-seize lubricant on spark plugs can do more harm than good, which is why it’s important to check the manufacturer’s specifications on spark plug maintenance.
Rookie Mistakes When Replacing Spark Plugs
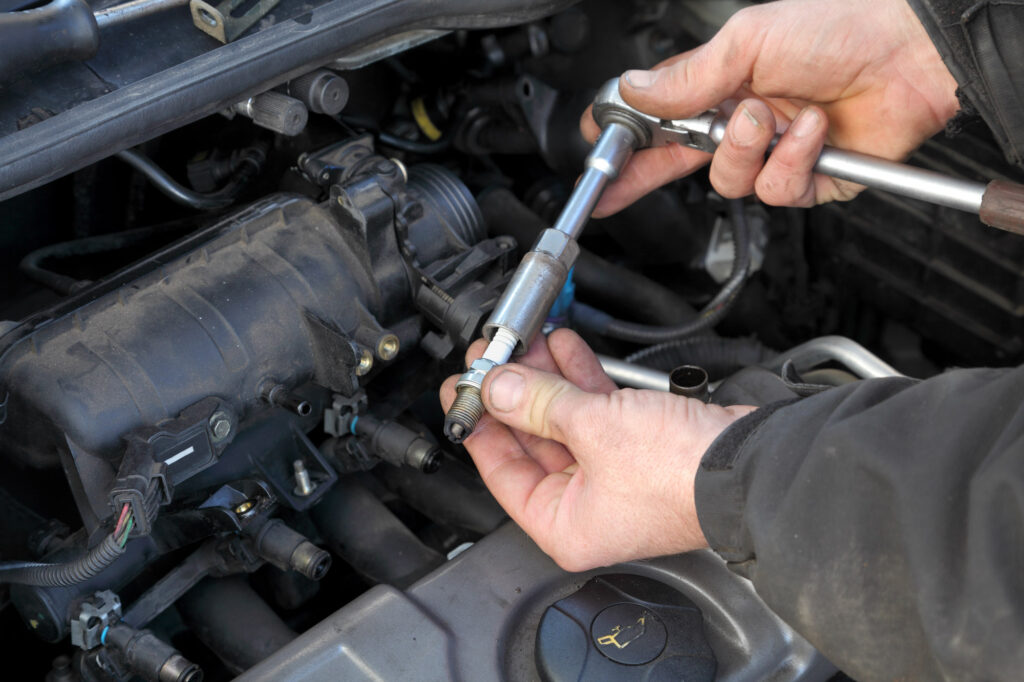

Spark plug replacement might seem like a simple task, but even a professional who’s careless about precautionary measures can end up committing critical errors while doing the job.
Here are some of the most common mistakes when replacing spark plugs.
Mistake #1: Replacing a Faulty Spark Plug While the Engine Is Hot
Working with a hot engine while replacing a bad spark plug increases the risk of getting burned and damaging the spark plug thread. So, if you’re replacing a spark plug, make sure to let the engine cool down before doing so.
Mistake #2: Working In a Contaminated Environment
When replacing a spark plug, make sure to clean your area immediately after taking out the ignition coil. Otherwise, you run the risk of having a contaminated combustion chamber.
Mistake #3: Using the Wrong Tools
Using the wrong tools can cause the spark plug to fall out of its socket or tilt during installation, damaging the spark plug or cylinder head. So make sure to use the appropriate spark plug wrench or special socket when replacing the spark plugs.
Mistake #4: Applying Anti-Seize on the Spark Plug
Using oil and other types of lubricating grease can damage the spark plug or cylinder head.
Mistake #5: Failure to Use a Torque Wrench
Without a torque wrench, you run the risk of damaging the spark plug and cylinder head during installation. You might even damage the engine if you’re not careful.
When installing a new spark plug, tighten it with your hands first before using a torque wrench. Apply the right amount of torque using the specifications on the packaging and stop at the click sound.
Mistake #6: Cleaning a Spark Plug Instead of Replacing It
Always replace contaminated or damaged spark plugs. Simply cleaning and cleaning them can cause problems down the line.
Also, keep in mind that the condition of spark plugs can help you determine the condition of the engine as well. Spark plugs covered in soot are a common cause of excessive idling, a defective thermostat, a rich air-fuel mixture, or a weak ignition system output.
Meanwhile, a spark plug covered in oil could mean that there’s a worn-out or broken piston ring, worn valve guides, or defective or missing valve stem seals.
Mistake #7: Choosing a Spark Plug Replacement Based on External Appearance
Installing a spark plug replacement based on shape or thread length alone won’t guarantee its proper operation. In some cases, the spark plug can wear prematurely.
Always refer to manufacturer-recommended specifications when choosing a spark plug replacement.
Mistake #8: Failure to Replace the Entire Spark Plug Set
Always replace spark plugs as a set instead of replacing them one by one to prevent inconsistent performance and engine misfires.
Mistake #9: Reinstalling Used Spark Plugs
Reinstalling used spark plugs can cause their sealing ring to come loose, which can eventually lead to engine damage.
Mistake #10: Pulling Spark Plug Cables
Pulling the spark plug cable can break the connection between the internal wire and metal connector, resulting in an open circuit or partially closed connection that works intermittently.
A damaged spark plug wire will usually cause the boot to separate from the wire, making the damage visibly possible to diagnose.
Where to Get Replacement Spark Plugs for Your Vehicle
If anti-seize compounds render your spark plugs inoperative, it’s important to get a replacement as soon as possible. Luckily, you can find what you need at CarParts.com in no time.
The best part? You can get your hands on some new spark plugs without leaving your home. Simply use your mobile device or computer to visit our website. Use our vehicle selector to find spark plugs that are compatible with your ride.
We make sure to get our spark plugs from some of the most trusted manufacturers in the industry. Every item in our catalog is carefully vetted by a team of professionals, guaranteeing both quality and longevity. You won’t have to worry about your new spark plugs failing you any time soon.
On top of that, our warehouses are located all over the US, meaning you can receive your order within days. You can also save a lot of money because our products are available at competitive prices.
Check out our catalog today!
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.