Automatic transmissions are able to shift gears due to solenoids that manage the movement of fluid between various hydraulic circuits. When these solenoids malfunction, the P0751 code might appear once you plug in a scan tool.
What Does the P0751 Code Mean?
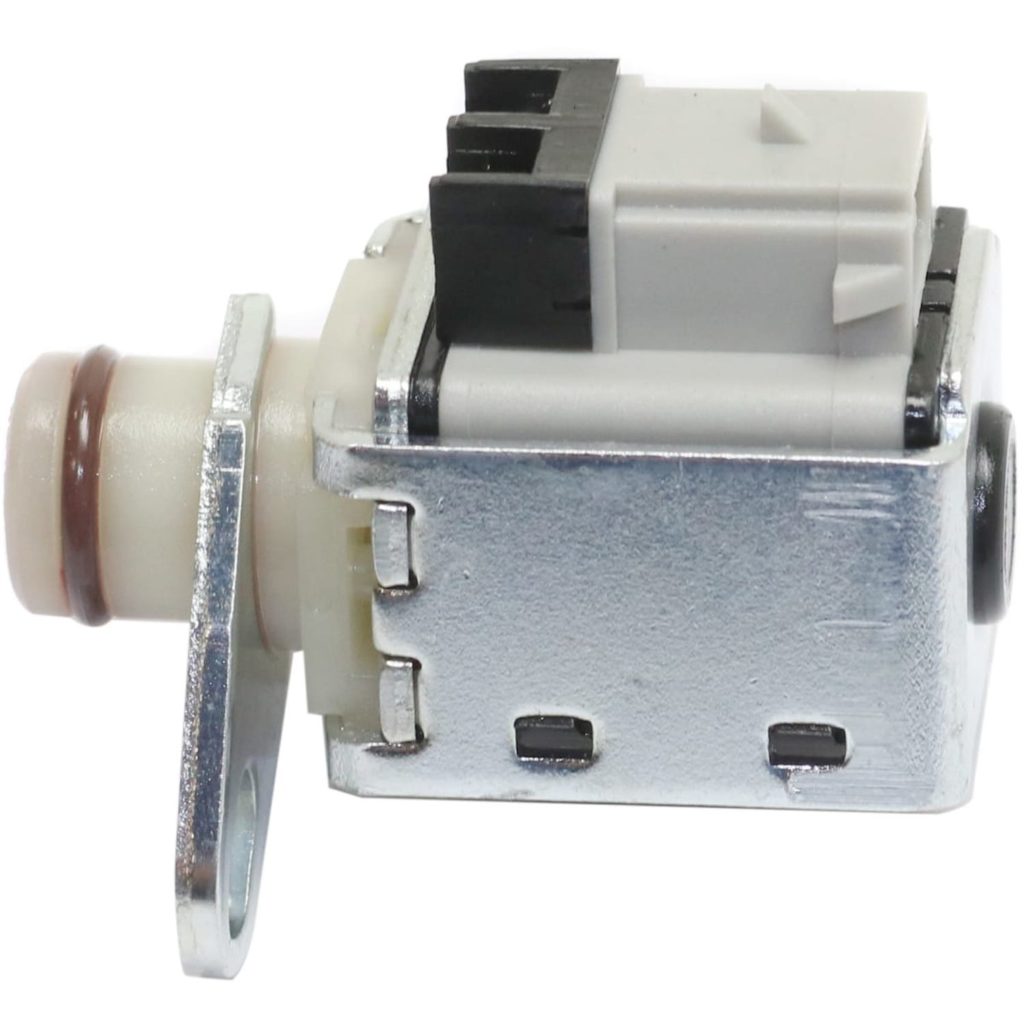
The P0751 is defined as “Shift Solenoid “A” Performance/Stuck Off.” Shift solenoids are used to deliver the appropriate torque that you require by changing the transmission’s gears. The P0751 code triggers when the shift solenoid “A” shift circuit has a malfunction and the PCM detects it.
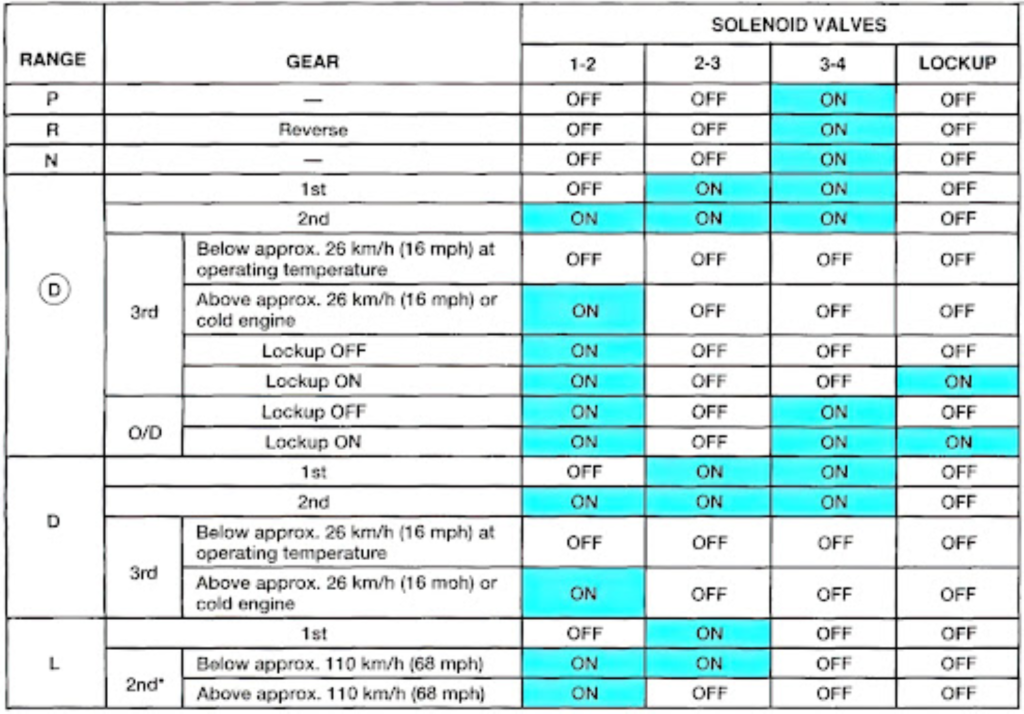
There are typically three shift solenoid circuits in a vehicle and they’re categorized as A, B, and C, 1, 2, and 3, or 1-2, 2-3, and 3-4. Many modern transmissions have more than three solenoids. The P0751 code specifically identifies that the “A” solenoid circuit has the issue.

If you’re planning to do DIY diagnostics or troubleshooting, make sure to read our technical discussion about shift solenoids.
What are the Possible Causes of the P0751 Code?
This code triggers when the PCM detects shift solenoid “A” shift circuit has a malfunction. The cause of this malfunction can be attributed either to low or dirty transmission fluid, or a clogged transmission filter. It can also be caused by transmission shift solenoid failure, transmission failure, or transmission control module (TCM) failure. The P0751 code can also be triggered by corroded or damaged connectors or faulty wiring.
What are the Common Symptoms of the P0751 Code?
The most common signs of a P0751 code include:
- Transmission slipping
- Transmission overheating
- Transmission gets stuck in gear
- Decreased fuel economy
- The vehicle enters limp mode
- Check engine light
How to Diagnose the P0751 Code
While we know that the PCM is identifying a shift solenoid problem, identifying which part is broken might be difficult because the shift solenoid might not be the cause. Vehicle transmissions are located under the vehicle and often need a lot of labor to repair. To get a proper diagnosis, you may want to consult a professional. If you’re interested in knowing whether or not your P0751 code is caused by a faulty solenoid, you can check out the video below.
How to Fix the P0751 Code
Before you perform any repair, you’ll need to accurately diagnose the issue that’s triggering the code. But there isn’t usually an all-encompassing fix for any OBD-II diagnosis. Since there’s a variety of possible causes, it also means that there are many ways of fixing them.
Once you’ve identified the issue causing the P0751 code, you can then consult online auto repair resources and how-to guides for possible solutions.
All vehicles are different. This means a repair for an OBD-II code for one vehicle may not be applicable for another. As a result, you should consult your vehicle’s repair manual when it comes to troubleshooting and repairing diagnostic trouble codes. Chilton repair manuals may also be useful. However, ALLDATA subscriptions are even better, as they provide detailed factory repair information for drivers who want to do repairs themselves.

Other Notes About the P0751 Code
The code’s definition may immediately point towards a faulty shift solenoid. However, the code can also be triggered by dirty transmission fluid, or the other causes listed above. Sometimes, immediately replacing the solenoid might not be the most effective course of action. The solenoid might need to be tested to make sure that it’s the faulty part that’s triggering the code. Failure to follow the correct inspection procedure might result in owners immediately replacing the solenoid when it isn’t always necessary. Many vehicle makes like Chevrolet, Ford, and Lexus can be affected by the P0751 code.
A Closer Look at Shift Solenoids
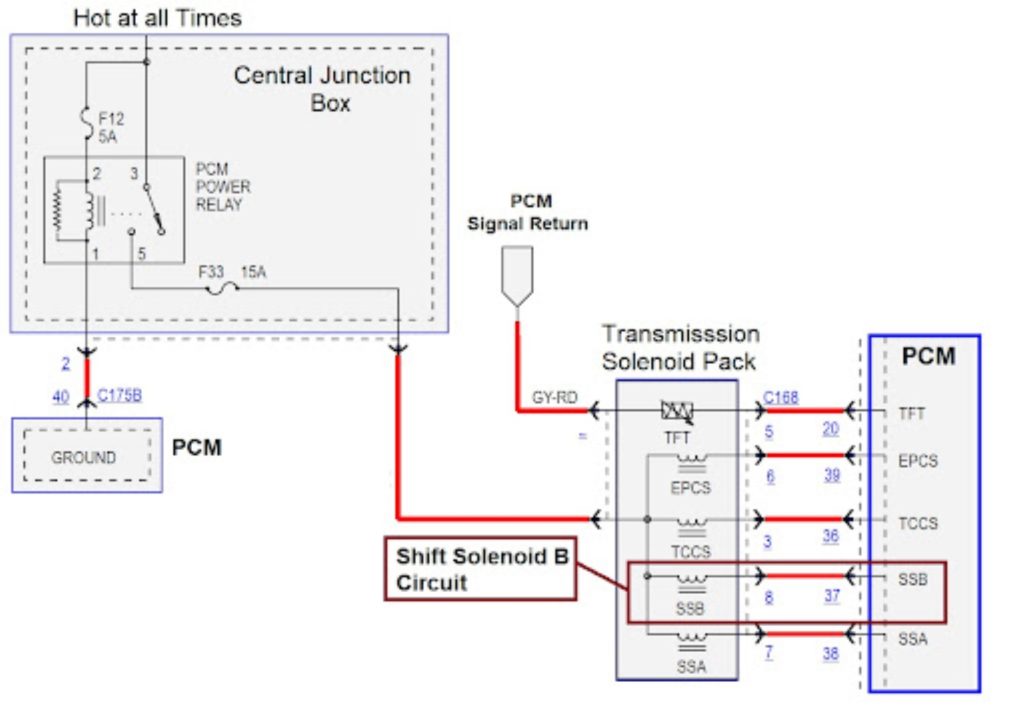
Shift solenoids are either hard-wired to power and triggered by a ground from the TCM/PCM controller or they’re hard-wired to ground and receive power from the controller. Typically, a shift solenoid, when not energized, leaks fluid pressure. But when the solenoid is energized, the fluid leak is blocked and pressure rises in a channel to move valves and/or apply transmission components.
Since certain measurable things are supposed to happen when a shift solenoid is energized, the TCM/PCM watches for those things to take place: changes in certain shaft speeds, engine load change with a gear change, etc. So if there is no detectable electrical fault in the solenoid circuit and yet speed and load changes indicate the solenoid isn’t functioning when energized, that’s typically referred to as a “performance” fault.
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.


















