The camshaft position sensor (CMP) and crankshaft position sensor (CKP) are important components because they allow the engine control module (ECM) and transmission control module (TCM) to track the engine’s RPM. In some cases, problems with these sensors can lead to transmission-related symptoms. Connect a scan tool to check if your vehicle’s ECM has stored the P0726 code.
What Does the P0726 Code Mean?
Diagnostic trouble code P0726 is defined as Engine Speed Input Circuit Range/Performance.
During acceleration, the transmission shifts up the gear range. This allows the vehicle to reach higher speeds with less RPM, which prevents excessive fuel consumption and engine wear. However, lowering the engine’s RPM will result in the driver having less available power and torque.
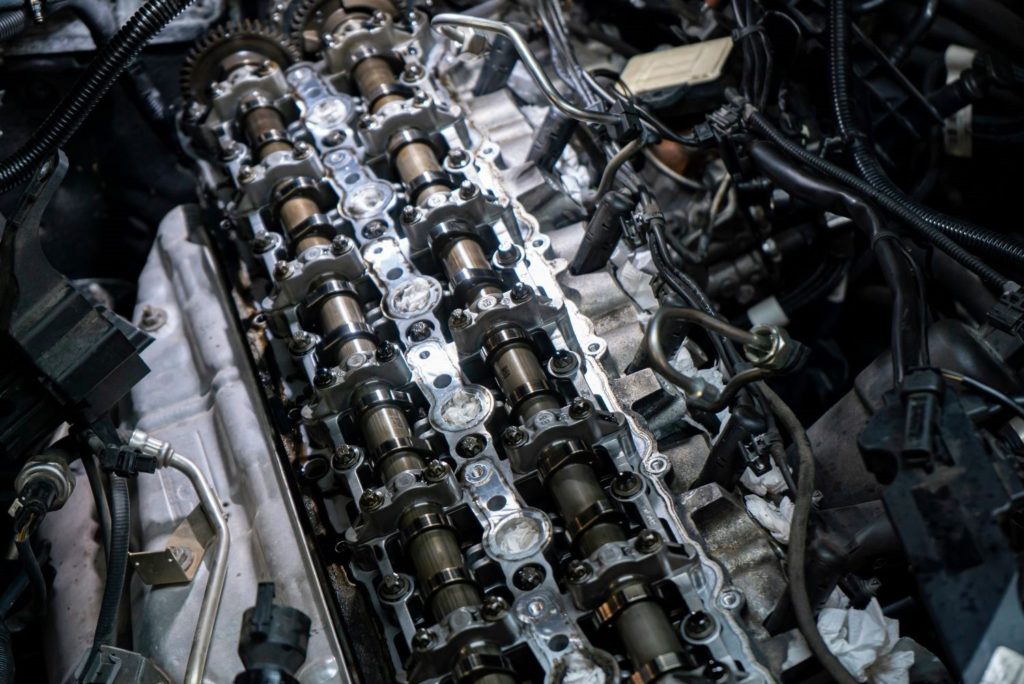

Depending on the driver’s throttle input, the TCM will determine the appropriate shift timing based on variables like engine RPM and vehicle speed. For the transmission to determine the right gear relative to the driver’s inputs, it needs to account for engine RPM because it’s a major factor in how much power and torque the engine can produce. Engine RPM is measured by the CKP and CMP sensors.
In place of a dedicated engine speed sensor, the TCM sometimes receives the engine speed signal from the engine control module (ECM) over the data network. Code P0726 is set when the TCM doesn’t receive the expected engine speed signal.

Note: The definition of the P0726 code can be different depending on the vehicle manufacturer. Consult the appropriate repair manual or repair database for the exact code definition.
What are the Common Causes of the P0726 Code?
The issues that trigger the P0726 code can be caused by the following problems:
- Faulty CKP or CMP
- Faulty transmission output speed sensor
- Damaged or worn engine speed sensor reluctor ring
- Mechanical transmission failure that causes transmission slippage
- Faulty TCM
- Faulty ECM
- Circuit problems, such as a damaged wire or poor connection
What are the Common Symptoms of the P0726 Code?
Your vehicle might exhibit the following symptoms if the P0707 code has been stored:
- Decreased fuel economy
- The transmission erratically shifts
- Malfunctioning tachometer
- Malfunctioning speedometer or odometer
- Transmission slippage or delayed engagement
- Check engine light
- Vehicle stuck in limp mode
How to Diagnose the P0726 Code
The P0726 code concerns several complex components like the transmission, transmission sensor, and TCM. This code is known to be commonly caused by specific issues, but you should still check if your vehicle has them before proceeding with repairs.
When it comes to troubleshooting any diagnostic code, always remember that procedures vary depending on vehicle specifications. If you aren’t familiar with the troubleshooting process, ask a trained mechanic to do the job for you.
How to Fix the P0726 Code
Fixing the problems that cause the P0726 code can be quite difficult if you don’t have the right tools and knowledge. It might be more convenient to simply bring your vehicle to your local mechanic for repairs. If you think you have the right knowledge and tools, then follow the appropriate steps and protocols to fix the problem without creating complications.
Remember that there isn’t any cure-all fix-all solution that can fix a trouble code in all vehicle models. Even mechanics sometimes rely on knowledge banks and online resources before conducting repairs. Chilton guides or an ALLDATA subscription contain vehicle-specific repair information, so you might want to check these out before starting the repair process.
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.


















