On-board diagnostic (OBD) codes are designed to help mechanics and vehicle owners identify potential problems with a vehicle. But before attempting any fixes to resolve these codes, it’s important to know exactly what they mean.
The P0082 code is one of thousands of error codes that may be set by your vehicle’s primary computer. If you’re having trouble figuring out what code P0082 means and how to resolve it, here is some basic information that may help you.
What Does the P0082 Code Mean?
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P0082 stands for “Intake Valve Control Solenoid Circuit Low Bank 2.” It may be set when the powertrain control module (PCM) perceives a potential issue with the signal from the intake valve control solenoid.
To be precise, P0082 may be logged if the PCM detects that the pulse width modulated (PWM) signal from the intake valve control solenoid in Bank 2 has a voltage lower than factory specifications.

Bank 2 refers to the side of the engine that does not have the #1 cylinder. Meanwhile, the intake valve control solenoid can be found on the intake manifold side of the cylinder head.
In vehicles with variable valve timing (VVT), the PCM operates a control solenoid to apply oil pressure to the actuator(s) on the end of the camshaft(s). Regulating oil pressure to the actuator changes the position of the camshaft, altering valve timing.
The PCM adjusts the opening and closing of the exhaust valve for fuel efficiency. However, if the PCM perceives a potential issue with the signal from the intake valve control solenoid on Bank 2, particularly detecting a voltage lower than the threshold, it will set code P0082.

Depending on the severity, other DTCs may also be logged. P0082 is similar to codes P0081, P0083, and P0028.
Note: The definition of code P0082 may be different depending on the vehicle manufacturer. Consult the appropriate repair manual or repair database for the exact code definition.
What are the Possible Causes of the P0082 Code?
P0082 is a generic code, so it can have several causes. Here are the most common:
- Extremely low engine oil level
- Damaged exhaust valve control solenoid
- Circuit issue
- Failing PCM
What are the Common Symptoms of the P0082 Code?
You may notice the following symptoms if you own a vehicle with a stored P0082 error code:
- Check engine light is on
- Poor engine performance
- Excessive fuel consumption
- Poor acceleration
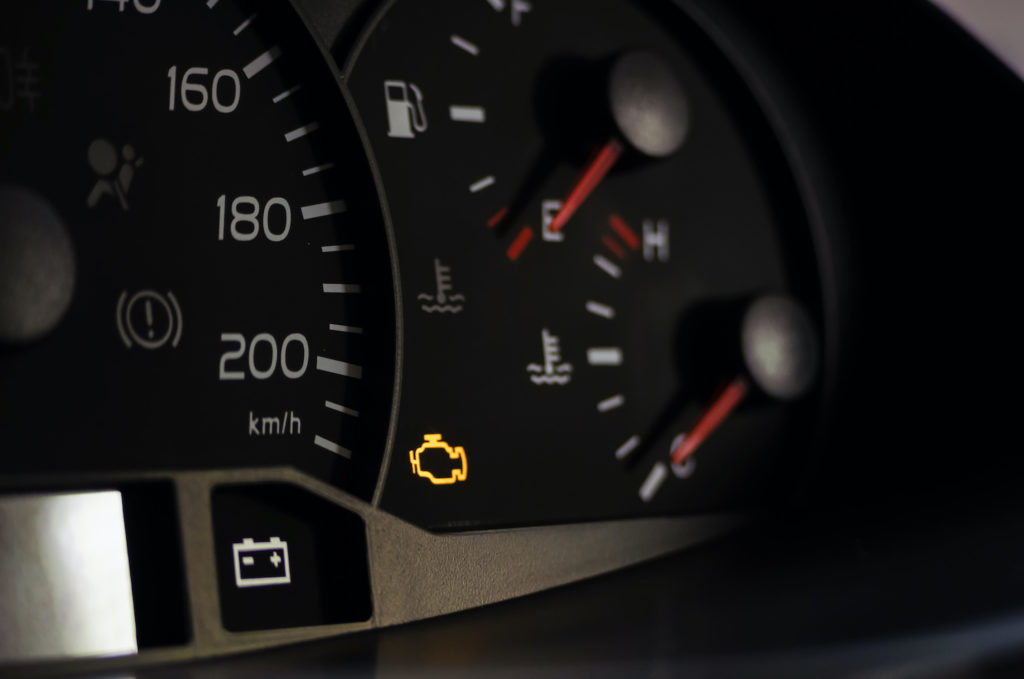

How to Diagnose the P0082 Code
Diagnosing code P0082 may be tricky, as it is a generic code with several possible triggers. As a rule of thumb, always follow the diagnostic procedure specified by your vehicle’s manufacturer. This is because the steps may vary per vehicle. For instance, the steps for diagnosing a code P0082 on a Subaru may differ from testing for a P0082 on a VW.
Refer to a repair manual for the most suitable diagnostic strategies. If you’re not well-versed in auto repair, it would be best to seek the help of a professional.
How to Fix the P0082 Code
Like other OBD-II codes, there is no fixed solution for code P0082. It shares similar causes and symptoms with other DTCs. However, that does not mean that it shares their fixes as well. All vehicles are different, so you should refer to your vehicle’s factory repair guide before troubleshooting the issue.
Code P0082 is a complicated code, so always consult a repair manual or repair database before attempting any fixes. However, if you’re not that confident in your automotive repair skills, it’s best to leave the repairs to a licensed mechanic.
Where to Get an Exhaust Valve Control Solenoid to Fix DTC P0082
Failing to address code P0082 can lead to several complications, from costly excessive fuel consumption to risky poor acceleration. If a bad exhaust valve control solenoid triggered the code, don’t put off replacing it. The great news is that finding a replacement solenoid is easy with the help of CarParts.com.
We make sure every item in our catalog is vetted by industry professionals to guarantee both quality and longevity. That means you won’t have to worry about your new solenoid malfunctioning anytime soon.
On top of that, you don’t have to wait long for your new exhaust valve control solenoid. Our warehouses are strategically located all over the US to deliver to ensure that customers get whatever they order as soon as possible. You also won’t have to worry about breaking the bank because our products are available at competitive prices.
To get started, use your mobile device or computer to visit our website. Then, fill out the vehicle selector to narrow down the selection to the solenoids that fit your ride.
Check out our exhaust valve control solenoids and shop now!
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.














