There are a variety of electronically-controlled suspensions in use today. Many of these systems use air springs and an air compressor to raise and lower the vehicle. A control module (computer) and sensors govern the compressor.
It’s not uncommon for an air suspension compressor to fail. Often, the failure occurs due to a leak somewhere in the system that overworks the compressor and causes it to burn out.
If your compressor isn’t working, it’s smart to perform some diagnostic work to ensure the compressor (rather than a circuit issue) is to blame.
How to Test an Air Suspension Compressor
The steps for testing an air suspension compressor will vary depending on the vehicle and the system design. The information below is generic and for entertainment and educational purposes only. Be sure to follow the factory repair information for your specific application.
You can learn more about accessing quality repair information in this article.
With that in mind, let’s discuss the steps of a typical air compressor troubleshooting strategy.
Verify That the Compressor is Inoperative
First, verify that the compressor is indeed inoperative. Usually, you can do this by listening for it to turn on. Depending on the vehicle and the system design, you may need to perform some type of action, such as adding weight to the rear of the vehicle, to engage the compressor.
If you don’t hear the compressor running when it should, either the compressor is faulty or there’s a problem somewhere in its control circuit.

Check that the Compressor Has Power and Ground
Once you’ve verified that the compressor isn’t working, you need to find out why. Is the compressor faulty or is there a circuit issue preventing it from operating?
To find out, you’ll need a digital multimeter (DMM) and access to repair information that includes the factory wiring diagrams. Then, you can perform the steps listed below.
Tip: You can also test the compressor by jumping it with jumper wires or a Power Probe.
- Put on your safety glasses.
- Consult a repair manual to determine which terminals are which on the compressor electrical connector.

- Test the power side of the circuit by doing the following:
- Set your DMM to the DC volts setting.
- Disconnect the electrical connector going to the compressor.
- Turn the ignition on and ensure the vehicle is in a state where the compressor would usually be running.
- Connect the negative meter lead to a good ground (the battery’s negative terminal works the best). Connect the positive meter lead to the power feed terminal on the harness side of the compressor connector.
- If you see battery voltage (or close to it) on your meter, the power side of the circuit is intact.
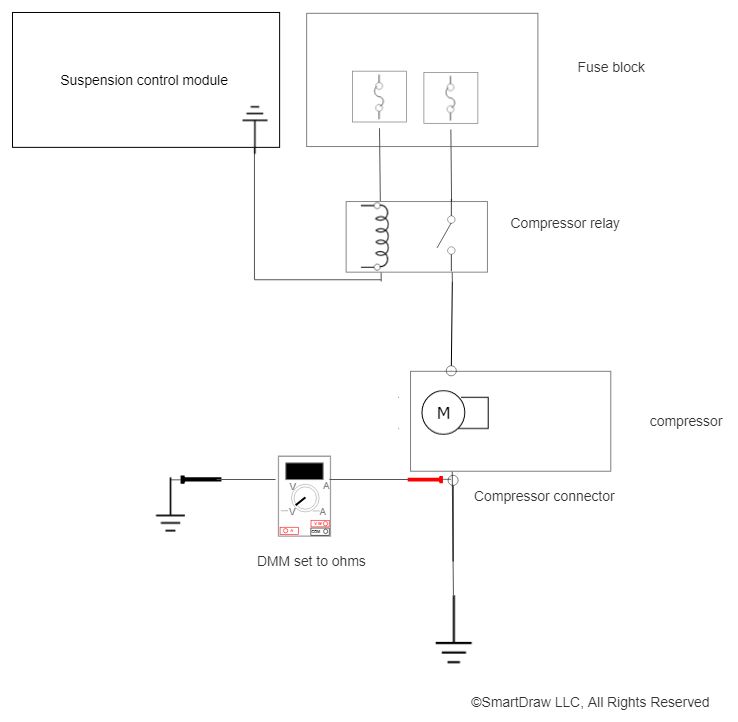
- Next, test the ground side of the circuit by doing the following:
- Make sure the vehicle’s ignition switch is turned OFF.
- Set your digital multimeter (DMM) to the ohms setting.
- Connect one meter lead to a good ground (the battery’s negative terminal works the best). Connect the other meter lead to the ground terminal on the harness side of the compressor connector.
- A reading of anything other than out of limits (OL) indicates the ground side of the circuit is intact.
If you find both sides of the circuit to be intact during testing—but the compressor does not run when it should—then the compressor is likely faulty and should be replaced.
On the other hand, if you find an issue with the compressor’s control circuit, you’ll need to trace the wiring diagram and perform further testing. A problem with the power side of the circuit could indicate a failed relay, blown fuse, wiring/connector issues, or a problem with the suspension control module.
Meanwhile, an issue with the ground side of the circuit usually points to damaged wiring or a poor connection.
How to Test an Air Suspension Compressor Relay
A lot of people also want to know how to test an air suspension compressor relay. You can test the compressor relay with a fused jumper wire.
Be sure to take all of the necessary safety precautions if you decide to attempt this method.
Once again, the information below is generic and for entertainment and educational purposes only. Be sure to follow the factory repair information for your specific application.
Tip: You can also test the compressor relay by swapping it with a relay of the same design from another one of the vehicle’s circuits.
- Put on your safety glasses.
- Consult a repair manual to determine which terminals are which on the relay.
- Remove the relay from the power distribution box.
- Bypass the relay by connecting a fused jumper wire between the terminals in the power distribution box for the switch (output) portion of the relay.
- If the compressor operates with the relay bypassed, the relay is likely faulty and should be replaced. It’s also possible that there’s a problem with the control side of the relay circuit. So, if replacing the relay doesn’t work, you’ll need to check the circuit.
How to Get Your Hands on a New Air Suspension Compressor
If your air suspension compressor is faulty, don’t put off replacing it. It can affect your suspension system’s performance, making it risky or uncomfortable to drive. On the bright side, getting your hands on a new one is easy with the help of CarParts.com.
The best part? You can get your hands on a new air suspension compressor without ever leaving your house. Use your mobile device or computer to visit our website. Then, enter your ride’s year, make, and model into the selector to view compatible compressors and change the search filters based on your needs. Check out securely, and wait for your new part — it’s that easy!
We only source our air suspension compressors from the most trusted manufacturers in the industry. They’re on hand, ready to ship from a warehouse near you, and available at competitive prices.
Don’t drive without a functional suspension system. Shop now to get your hands on a new air suspension compressor that’s built to last in no time!
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.