If your vehicle’s automatic transmission has jerky gear changes or erratic shifting, then it could be due to a faulty transmission speed sensor. If ignored, this can cause excessive fuel consumption or even transmission damage (although this is rare). In this article, we’ll discuss how the transmission speed sensor works and share some tips to help you determine whether it’s causing your vehicle’s problems.
How To Test a Transmission Speed Sensor
Testing a transmission speed sensor involves several important steps. If the scan tool you’re using provides datastream information on the sensors in question, this may be the only tool you need.
Diagnosing With a Scan Tool
Use a scan tool to check for error codes related to the transmission speed sensor, and again, check the sensor using the datastream. If the scan tool shows these codes and the datastream indicates intermittent, skewed output, or no output, then you’ll need to replace the sensor if the circuits check out. However, if there aren’t any codes present, you’ll need to diagnose the issue by testing the sensor and ruling it out of the equation.
Locating the Transmission Speed Sensor
Where is the transmission speed sensor located? This will require research to make sure you aren’t working on the wrong sensor. There is no pat answer that will help you find the sensor on just any and every vehicle, but you can find the location of the sensor on your vehicle online.
But as an example, on some Hyundai vehicles like the Elantra, the sensor will be located behind the valve body, which requires you to drain the vehicle’s transmission fluid and get the valve body out of the way. You’ll only see the wiring harness and speed sensors once the valve body has been removed.
Meanwhile, a 2001 to 2005 Ford Explorer’s speed sensor is accessible from outside the transmission case. To reach it, you’ll need to raise your vehicle and look for the wiring harness outside the transmission case. The wiring harness will lead to the speed sensor located on top of the transmission case.
Disconnecting the Sensor
You’ll need a socket wrench to remove the transmission speed sensors that are bolted onto their mounting point.
After the bolt is removed, use some elbow grease to free the sensor. Sometimes, you’ll need to gently pry it out using pliers. Be careful when you do this, because some fluid can leak out from where the sensor is inserted.
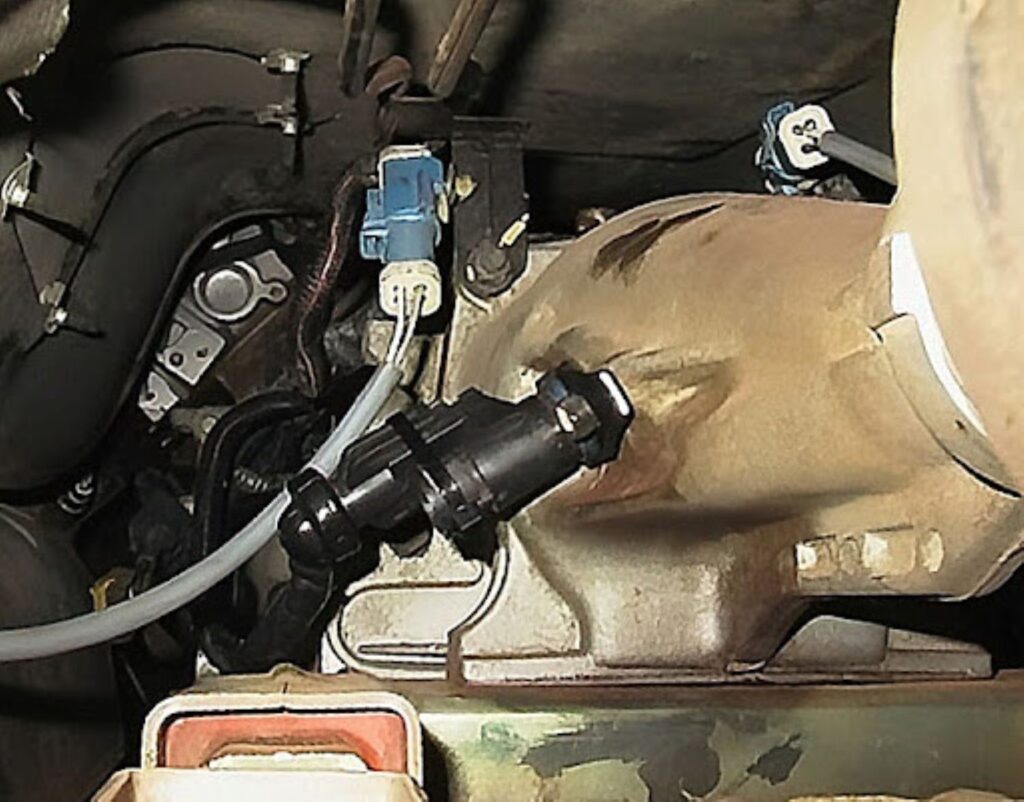

Testing a Transmission Speed Sensor
If you can get to the sensor terminals, you don’t have to remove the sensor to test it. You can unplug the sensor and measure the resistance if it’s a variable reluctance sensor with a copper winding and a magnet. You can measure the output of the sensor as AC voltage.
Caution: Don’t do this if you don’t know how, and don’t ever work on any vehicle that isn’t properly and safely supported.
If it’s a Hall Effect sensor, you’ll need to use a scope rather than measuring the sensor resistance. A scope is something that’s not usually available in a DIY garage.

Inspecting the Wiring Harness
The wiring that connects to the sensor is equally important. Inspect the wiring for any fraying, damage, or exposed conductors. Damaged wiring can also compromise the sensor’s function, so you’ll need to replace the wiring for the sensor to give accurate readings.
Troubleshooting a faulty transmission speed sensor can be a difficult task, especially if you aren’t familiar with your vehicle’s transmission or with the various different types of sensors. If you have trouble following the diagnostic steps in this article, we recommend you leave the task to a professional.
What Does a Transmission Speed Sensor Do?
Electronic transmissions are usually equipped with multiple transmission speed sensors that report to the ECM/PCM/TCM how fast the input and output shafts of the transmission are spinning. The torque converter turbine is splined to the transmission input shaft, also known as the “turbine shaft.”
The transmission input speed sensor measures the speed of the input (turbine) shaft, which transfers power from the engine to the transmission. The output speed sensor measures the speed of the output shaft, which connects the transmission to either the differential on front wheel drive vehicles or the driveshaft on rear wheel drive vehicles.
Some transmissions may have a speed sensor for one or more of the transmission’s internal intermediate shafts as well, so the number of sensors varies widely from platform to platform.
The ECM or TCM knows how fast each shaft should be spinning in each gear, factoring in the speed of the turbine shaft and whether or not the torque converter is modulating, locked, or spinning freely. The gear ratios and the different shaft speeds corresponding with these ratios are written into the computer’s algorithms for feedback and comparison.
The control module (ECM/TCM/PCM) compares crankshaft rpm, turbine shaft (transmission input shaft) rpm, intermediate shaft where equipped, and output shaft rpm. It knows what gear it is commanding and it knows if the gear it has commanded is in play based on input from the sensors.
Transmission shaft speed sensors can be inductive sensors (magnet with a wire coil surrounding it) that produces an AC analog wave, or the sensor can be digital (Hall Effect) that produces a square wave. The sensor typically reads steel teeth moving past the sensor as the shaft spins.
Getting Your Hands on a New Speed Sensor
If you’ve tested your speed sensor and learned that it’s indeed been rendered inoperative, it’s important to do two things: find the source of the problem and replace the speed sensor as soon as possible.
Replacing a bad speed sensor is crucial because driving with one can lead to many problems. For example, without a functional speed sensor, you won’t be able to know how fast your vehicle is going. The anti-lock braking system also won’t activate properly, putting you in active danger every time you drive.
Finding a replacement speed sensor that’s compatible with your vehicle can be tricky. Fortunately, CarParts.com is here to help.
The best part? You don’t need to leave your home to get a new sensor. Simply input your ride’s details into our vehicle selector tool to view direct-fit parts, then use the search filters to find the ones that match your preferred price, brand, and specs. Place your order, and wait for it to arrive at your doorstep—it’s that easy!
Our auto parts are carefully selected by a team of professionals to guarantee both quality and longevity. You won’t have to worry about your new speed sensor failing you any time soon.
Don’t put yourself at risk by driving without an operative speed sensor. Shop now to get your hands on a replacement that’s built to last with CarParts.com.
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.