What Is a Rubber Grommet?
Also known as an edging or bushing, a rubber grommet refers to a small tube covering a panel hole’s sharp edges. It grips and protects wires, cables, and other components that pass through the hole from snagging on the rough edges.
Most rubber grommets are made of synthetic rubbers, such as neoprene, nitrile rubber, and silicone. They come in different shapes and sizes, ensuring a perfect fit for a variety of parts.
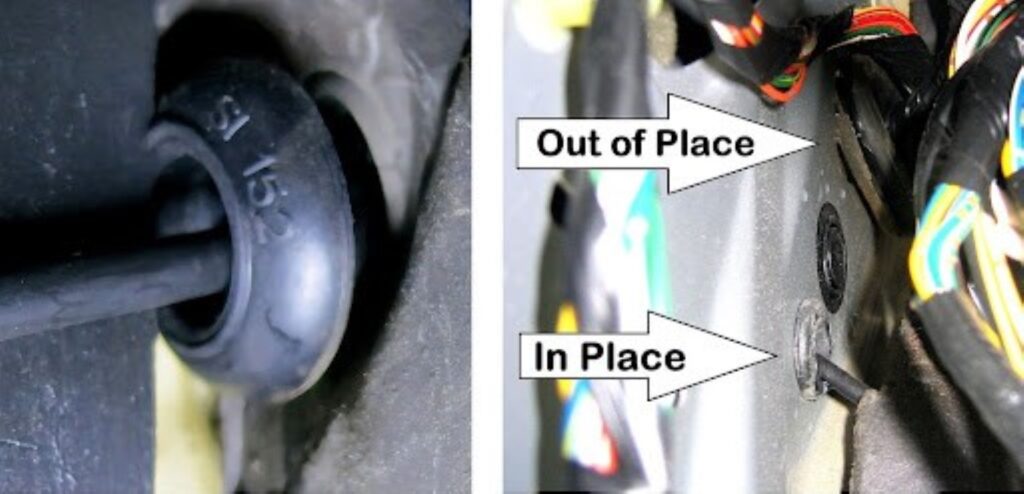
What Are Rubber Grommets For?
Because they’re highly resistant to temperature, wear, and chemicals, rubber grommets are perfect for automotive use. Here are some examples:
Electrical Wiring and Hoses
Rubber grommets also protect electrical wiring and fluid hoses from extreme temperatures, moisture, and other contaminants that can cause wear. This helps each part function better as well as extend its lifespan, making rubber grommets a worthy investment.
Other Applications
Other parts that use rubber grommets include firewalls, washer tanks, A-pillars, and fuel pumps.
Tips on How To Remove Rubber Grommets
While automotive grommets are specifically designed to be heat resistant, they aren’t invincible. Extreme heat can gradually cause the synthetic rubber material to degrade or melt, leaving your spark plug wire unprotected. If this happens, you’ll have to remove the damaged grommet before replacing it with a new one. Here are some helpful tips:
Prepare the Necessary Tools
You’ll save yourself a lot of time by preparing everything you need beforehand. To remove melted grommets, you’ll likely need a flathead screwdriver and a razor blade. You could also just use your fingers on most bulkhead grommets.
Let the Engine Cool
Tinkering under the hood when the engine’s still hot is a recipe for disaster (tinkering under the dash on the bulkhead, not so much). Even if you wear safety gloves, you can still risk burning your skin. Turn your engine off, and wait until it’s cool enough to touch.
Cut if Necessary
In some cases, you might have to cut the rubber in order to dig it out. Carefully cut it with a razor blade until you can fish it out with your pliers or picks.
Replace Any Damaged Parts
If you notice any other issues, you might have to replace other parts as well. Ask a mechanic to take a look before removing anything else. For example, you might need a new valve cover gasket if there’s an oil leak.
How Much Does a Grommet Replacement Cost?
The exact price will vary depending on several factors, including your vehicle’s year, make, and model. In general, however, rubber grommets are relatively affordable. You can buy high-quality rubber grommets for $10 to $30.
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.