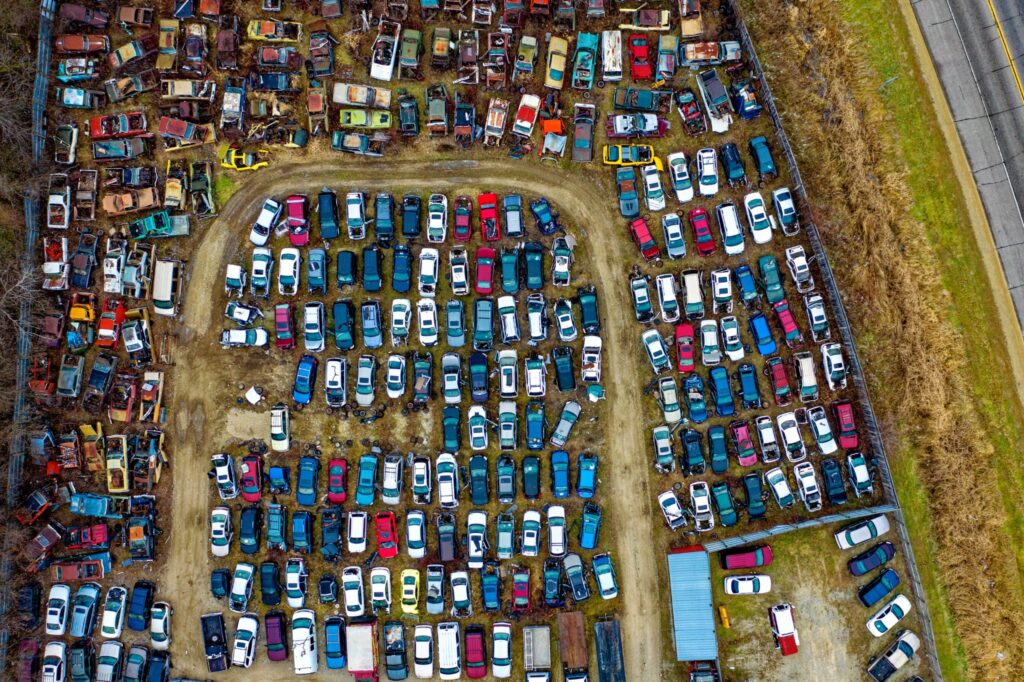
With millions of new vehicles rolling out of their respective factories each year, consumers are bound to discard their old daily drivers to get their hands on the latest models. And while top-selling automakers enjoy rocketing sales, junkyards are filled with piles of unused vehicles waiting to be crushed or recycled.
Auto recycling is quite complex. It doesn’t work the same way as sorting out your garbage and identifying which ones are biodegradable and non-biodegradable.
This article will walk you through the auto recycling process and help you understand which factors to consider before you recycle your vehicle.
By the Numbers
Approximately 27 million cars are recycled annually. For the average vehicle, about 90% of its parts can be recycled, including tires, metal, glass, plastics, and the engine.

On average, 14 million tons of steel are recycled from end-of-life cars.
Aside from these, liquids一including gasoline, diesel, and coolant一are also recycled.
- 100.8 million gallons of gasoline and diesel
- 24 million gallons of motor oil
- 8 million gallons of coolant
- 4.5 million gallons of windshield wiper fluid
But what about the remaining 10% of car parts that are deemed non-recyclable?
The truth is, the remaining 10% can still be recycled when you put them through the shredder. Such scraps can be used to make caps and covers for landfills.
The Car Recycling Process
Here are the general steps involved when recycling an old car.
Depollute
Before anything else, old cars that are up for recycling must be depolluted. During this process, combustible fluids like gasoline, coolant, and engine oil are removed from the vehicle to ensure that there will be no chemical leaks.
Dismantle
The vehicle is then dismantled, with functional parts like the engine and transmission taken apart and inspected. If such parts are still in good working condition, they can be sold in salvage yards or auto parts stores.
Once the functional parts have been removed, auto recyclers can now proceed with crushing the vehicle.
Sort
Scrap dealers will usually pick up metal parts from the dismantled vehicle and turn them into new products.
Meanwhile, parts like glass and plastic are sold to companies that can reuse them. Scrap glass is usually melted to create new windows and windshields.
Rubber is also another material that can be recycled from cars, particularly tires. Old tires are typically shredded and grinded to make new tires, and tire treads.
Battery Recycling
Unlike the other scrap parts mentioned in this article, the battery deserves a special section because recycling it can be a bit tricky.
About 96% of all lead acid batteries are recycled, but the process is a bit meticulous when it comes to handling them.
Batteries contain lead and other heavy metals that are dangerous for people and the environment. When taking them out, it’s important for the batteries to be stored in a sealed plastic bag and carried in an upright position to ensure that no acid will leak out of them.
To get the most out of old batteries, their lead material must be melted and sold after solidifying. Other components, such as sulfuric acid, get neutralized or converted into other chemicals like sodium sulfate.
Batteries that are taken from internal combustion engines require a meticulous recycling process that ensures almost everything that makes them up can be reused.
Unfortunately, the same thing can’t be said about the batteries from hybrids and fully electric vehicles.
Currently, only about 30% of EV battery content can be recycled. The rest will go to waste.
Auto Recycling Can Help In More Ways Than One
It’s no secret that recycling can positively affect the environment. Reducing waste and repurposing old materials provide an avenue of opportunities that go beyond environmental benefits.
The need to recycle over a billion tons of scrap parts has created countless job opportunities. In the UK alone, almost 800,000 employees are working in the automotive industry.
In addition, old parts have value no matter how little. This can serve as a motivation for car owners to properly recycle their vehicles.
Trash to Cash
You’re already disposing of your old car because it’s given you countless problems that end up with expensive repair bills.
And since your vehicle is headed for the junkyard, why not make a profit out of it?
A lot of local auto parts stores, scrap yards, and other shops will be willing to get your old car off your hands for a price. Here’s how much you can sell used car parts for.
- Car batteries – $5-$10 (the more batteries you bring, the higher you can sell them for)
- Oil and oil filters – 50 cents per gallon
- Tires – $25-$75
- Catalytic converters – $45-$100
- Glass – $25-$100
- Starters and alternators – $2-$10
- Scrap metal – 25-50 cents per pound
Remember to Do These Things Before Recycling Your Car
Once you’ve made up your mind about recycling your vehicle, make sure to remember the following:
- Check your trunk, glove box, and other storage compartments for personal items.
- Remove electronic devices that might still be of use to you when you get your new car. These include phone cables, dash cameras, and other plug-in items.
- Remove your license plate.
- Prepare your keys and your vehicle’s paperwork. These will come in handy when you’re dealing with titles.
Wrapping Up
Car recycling is a tedious process that aims to breathe new life into old parts. Generally, automotive recycling involves depolluting the vehicle, dismantling it, and sorting out individual parts to find out where they can be sold.
Should you want to pull apart your vehicle on your own, parts like tires, cat-cons, the engine, as well as oil filters can be sold at a reasonable price.
Lastly, regardless of whether you’re taking your vehicle to a recycling shop or dismantling it from your own garage, always make sure that there are no valuable items left behind.
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.