Motor oil plays an important role in keeping engine parts working under proper conditions. It helps lubricate moving parts, cool engine parts, reduce friction, and prevent rust and corrosion from forming on the surfaces of metal parts.
Changing or topping up on engine oil is part of your vehicle’s periodic maintenance. And most of the time, you’ll be left with a few quarts of extra motor oil lying around after you’ve changed your oil.
While you can keep your remaining motor oil until your next oil change, there might come a time when those extra quarts won’t be as effective as before due to various reasons. Read on to find out more about your motor oil’s shelf life, the factors that might speed up its expiration process, and more.
Does Motor Oil Have an Expiration Date?
Yes, it does. But keep in mind that it takes more than simply checking the expiration date to determine whether or not the motor oil is usable.
Does Motor Oil Expire After Opening?
Yes, it will, either due to it reaching its expiry date or other factors.

Note that even motor oil that’s kept inside the container can expire before its due date if it’s been exposed to extreme temperatures. So make sure to store your remaining motor oil in a cool and dry area.
An open container also increases the risk of contamination and leads to reduced effectiveness.
Shelf Life for Motor Oil
According to some leading oil companies, an unopened container of motor oil that’s been kept out of extreme heat can last between two and five years.
Improper storage can reduce your motor oil’s shelf life. Other than that, keep in mind that the shelf life for motor oil also varies depending on its type.
Conventional motor oil isn’t as refined as synthetic oil, so it has a shorter lifespan.
Synthetic motor oil is distilled, purified, and broken down to a basic molecular level. Because of these processes, the molecules of synthetic motor oil are more adaptive to temperature changes, which helps the oil last longer.
Additives, such as viscosity index (VI) improvers, antioxidants, and antiwear additives, also enhance the performance of synthetic motor oil. These ingredients help improve and protect the base oil and engine.

When Should You Replace Your Motor Oil?
Oil change intervals vary depending on your vehicle’s specifications. To determine when you should change your car’s oil, consult the vehicle manufacturer’s service schedule located in your owner’s manual or supplemental service booklet.
As a rule of thumb, for engines using conventional motor oil, the oil must be changed every 3,000 miles. But for those using synthetic blends or fully synthetic motor oils, experts recommend oil changes anywhere between 5,000 and 15,000 miles.
Conventional vs. Synthetic Motor Oil
Motor oil is generally classified into two types and further subdivided into groups, according to the American Petroleum Institute (API).
Conventional Motor Oil
Conventional motor oil is derived from crude oil and is under group classifications I and II.
Its first group consists of mineral, non-synthetic base oil with little to no additives. The second group of conventional oil consists of mineral oil with additive packages. It’s considered the most common type of conventional oil used in engines.
Synthetic Motor Oil
Unlike conventional motor oil, synthetic motor oil is not a naturally occurring compound. It is a combination of crude oil and synthetic or artificial chemicals that behave similarly to conventional oil.
The API categorizes synthetic motor oil under group classifications III, IV, and V.
Synthetic oils under group III are hydrogenated synthetic compounds or hydrowaxes. They are also the lowest costing synthetic engine oil.
Synthetic oils under group IV are those made from mineral and monomolecular oil called polyalphaolefin (POA).
Lastly, those under group V are non-mineral sources such as alcohol from corn diesters of polyesters.
Choosing the Right Engine Oil for Your Vehicle
Aside from your vehicle’s year, make, model, and engine oil type, here are the other factors you should consider when buying motor oil.
Viscosity
Viscosity refers to the engine oil’s thickness and capacity to flow. You’ll want to choose the viscosity recommended by the vehicle manufacturer. Once again, you can find this information in your owner’s manual of supplemental service booklet.
Symbols
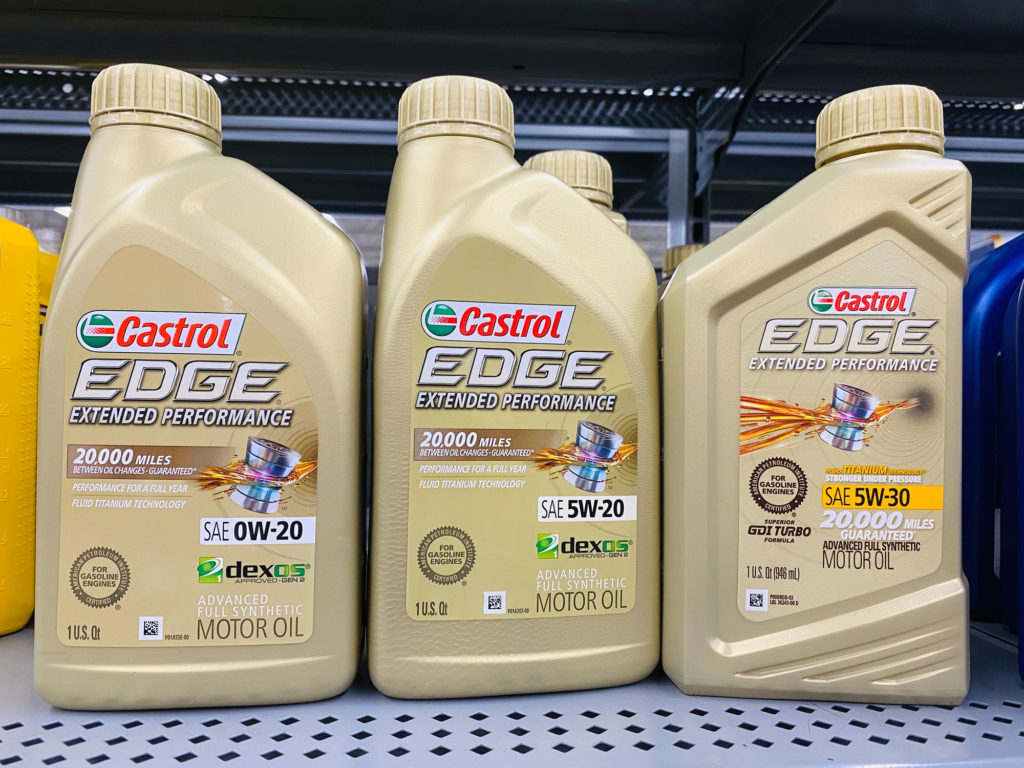

It’s important to check for certain certifications and ratings that authenticate the type of motor oil you’re planning to buy. Here are the logos you should keep an eye out for.
SAE Rating
Authentic engine oils come with a Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) grade number that indicates the oil’s viscosity range.
API Rating
Engine manufacturers and oil companies also have a partnership with the American Petroleum Institute (API) for proper testing and engine oil classification.
Before buying motor oil, make sure to look for the API doughnut symbol printed on the container. This means the type of oil you’re buying is satisfactory for use in an engine.
ILSAC Rating
The International Lubricant Standardization and Approval Committee (ILSAC) starburst symbol printed in front of the container symbolizes that the oil is suitable for use in almost any gasoline engine.
Where to Buy the Right Motor Oil For Your Vehicle
Using the motor oil that matches your vehicle’s specifications is critical for optimal engine operation. Fortunately, CarParts.com helps simplify the process of shopping for the products you need for an oil change online.
The best part? You don’t even have to leave your home to get your hands on new engine oil. Simply visit our website or download our app on your mobile device.
We carry high-quality yet affordable motor oils, so you won’t have to worry about breaking the bank. You can expect to receive your order within a matter of days, allowing you to save both time and money.
Don’t forget to change your motor oil regularly to keep your engine in tip-top shape. Shop and order the items you need for an oil change today!
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.