You stop by at a gas station to top up, only to find that your vehicle won’t take in more fuel. The fuel gauge indicates it’s not full, but for some reason, the gas won’t fill up the tank. Going to other stations leads to the same problem.
A car that won’t take gas is a frustrating problem, especially if you rely on it for your daily commute or have a long road trip planned.
Left unresolved, it can have you stopping by stations more often. Plus, if you’re driving in areas that have miles between gas stations, it can put you at risk of getting stranded in the middle of nowhere.
So what does it mean when your car won’t take gas even if the tank is empty or still has room for more?
Reasons Why Your Car Won’t Take Gas at the Pump
If the fuel tank won’t fill up, you might be dealing with a bad or clogged EVAP system, a blocked vent tube, or a malfunctioning gas pump nozzle.
Bad or Clogged EVAP System
The evaporative emission control system (EVAP) prevents gas fumes from leaking into the atmosphere. If any of its sensors (such as the fuel tank pressure sensor) act up, it can prevent fuel from filling properly.
Likewise, dirt and debris can accumulate and clog the hoses of an EVAP system.
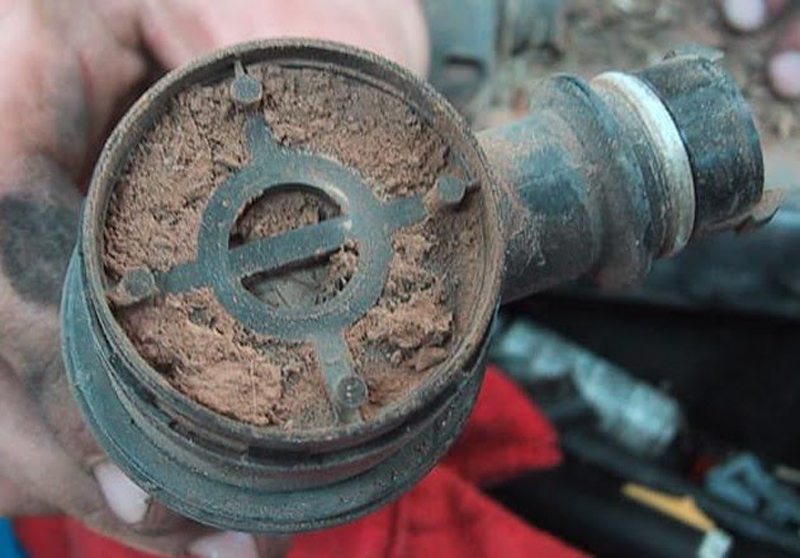

Blocked Vent Tube


Malfunctioning Gas Pump Nozzle
In some cases, there might be nothing wrong with your vehicle at all. Instead, there could be something wrong with the station’s gas pump nozzle.
If the nozzle is clogged or malfunctioning, fuel might struggle to come out, making it impossible to top up your vehicle. It’s a good practice to ask for help at the gas station just in case.
What to Do If the Car Won’t Take Gas in Tank
The solution depends on what caused the vehicle to stop taking gas. Did it happen suddenly or did you first notice it and then discover it was getting worse?
Some steps you can take once you encounter this problem include inspecting the gas pump nozzle and fuel cap. You can also clean the EVAP system. Note, however, that you have to know how to do this, and some EVAP systems are very complicated. Further, the clog may be somewhere you can’t see it.
Check the Gas Pump Nozzle
Observe the gas pump nozzle when you fill up your tank. If no fuel comes out, tell the attendant you need to use a different one.
Clean the EVAP System (if you know how)
Dirt and debris can interfere with your vehicle’s EVAP system, preventing it from working properly and stopping the fuel tank from filling up properly. You can try cleaning the EVAP system if you have the DIY knowledge and skills to do so.
Replace Bad Parts
If there are any damaged or faulty components in the EVAP system, they might be what’s keeping gas from entering the tank. Repairing or replacing them should fix the problem.
Components like the purge valve solenoid, the vent valve, and the charcoal canister can prevent the fuel tank from filling up if damaged. Ask a professional to inspect your vehicle and make recommendations if you suspect it has faulty EVAP system parts.
Where to Buy Replacement EVAP System Parts
If your vehicle isn’t taking gas due to inoperative EVAP system parts, it’s best to replace these parts as soon as possible. You can’t expect to run your vehicle without any fuel in its system, after all. Thankfully, you can turn to CarParts.com for quality EVAP system parts.
CarParts.com helps you order online with confidence. Not only do we have a wide range of quality aftermarket parts, we also offer them at various price points to suit different budgets. What’s more, our price match guarantee ensures you can always get the best deals. If you spot one of our EVAP system parts on a competitor’s ecommerce site for cheaper, hit us up. We’re happy to match or even beat their price on the spot.
Repair your vehicle’s inoperative components so it can take gas again. Order a replacement vapor canister purge valve or other EVAP system parts at CarParts.com now.
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.