Driving with bad wheel bearings can put you and your passengers’ safety at risk—it can cause your wheel and/or tire assembly to become loose.
To prevent this from happening, make sure that your wheel bearings are in good condition. Watch out for the following symptoms that may indicate a faulty bearing.
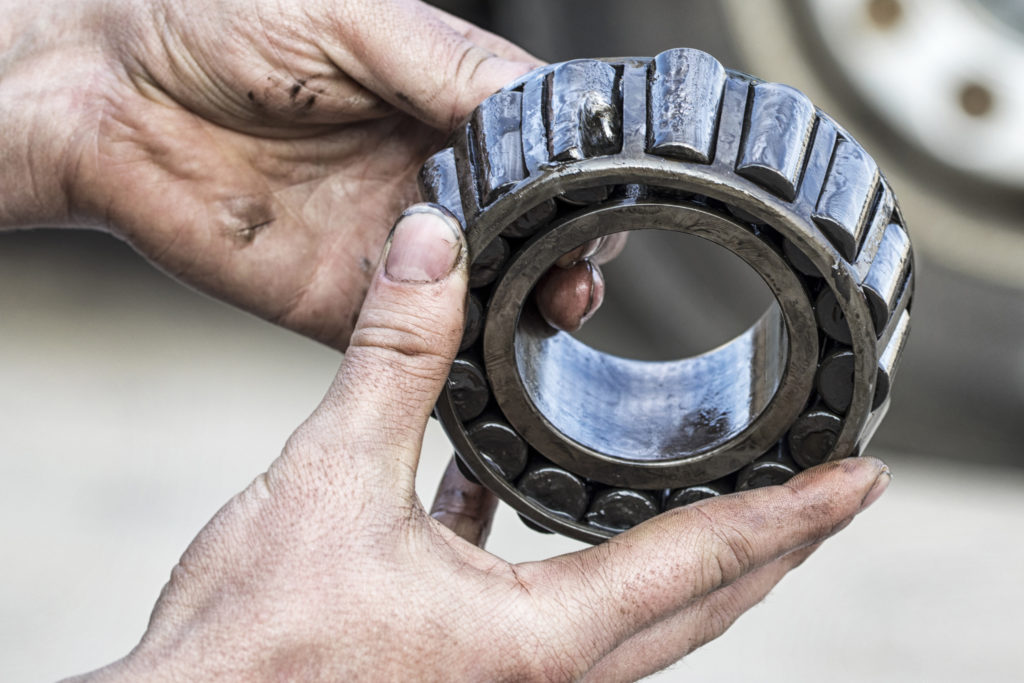

What are the Symptoms of a Bad Wheel Bearing?
Here’s a list of the most common bad wheel bearing symptoms:
Growling, Humming, or Rumbling Sounds
Unusual sounds coming from the wheel are often the first sign that something may be wrong with the vehicle’s wheel bearings. Bad wheel bearings produce noises that are often described as growling, humming, or rumbling sounds. In some cases, these failing parts may also produce a high-pitched sound.

It’s easy to overlook this symptom—especially if you often drive with loud music on. But the moment you turn the radio off, these noises become noticeable from behind the wheel.
Wheel bearing noises are typically in sync with the rotation of your tires. The sound may become noticeably louder as your vehicle accelerates. In some cases, the sound may also change depending on the direction of the steering wheel.
Take note, however, that these unusual sounds do not always mean that your bearings are faulty. Cupped tires and other wheel hub-related issues may cause similar noises.

Tire Noise vs. Bearing Noise
If the noises are different across varying road surfaces, there’s a good chance that the sound is being produced by your tires. However, if the sound remains the same, it’s likely caused by failed wheel bearings.
Another way to check the source of the sound is to temporarily overinflate your tires. If the wheels produce the same sound while you drive, the noise is likely coming from your wheel bearings.
Have your vehicle checked by a mechanic as soon as you notice unusual wheel noises. Even if the wheel bearings aren’t the culprit, it’s better to err on the side of caution and make sure that your wheels are in top condition.
Vibrations
Failing wheel bearings can make the steering wheel feel rough and cause excessive vibration when accelerating or cornering.

Play in the Steering
Another symptom that drivers may observe is looseness or excessive play on the steering wheel. This typically becomes more noticeable while driving over rough road surfaces.
Like other symptoms, steering difficulty may be caused by more than one faulty component. It’s best to take your vehicle to an auto repair shop for proper diagnosis.
Uneven Tire Wear
It is normal for tires to wear out because of prolonged use or unfavorable driving conditions. However, uneven tire wear may also be caused by faulty wheel hub components, such as loose bearings that may cause misalignment.
Abnormal tire wear may be caused by other suspension issues, so it is best to let a mechanic rule out other possible parts that may be causing your tires to wear unevenly.

Abnormal Side Pull When Braking
Faulty wheel bearings can cause your vehicle to pull to one side as you apply the brakes. However, take note that it’s also possible to experience abnormal side pull due to faulty brake components as well. For instance, a defective caliper or a worn-out rotor may cause similar issues.
If you’re not equipped with adequate knowledge and tools to identify the problem, let a mechanic troubleshoot your vehicle for you.
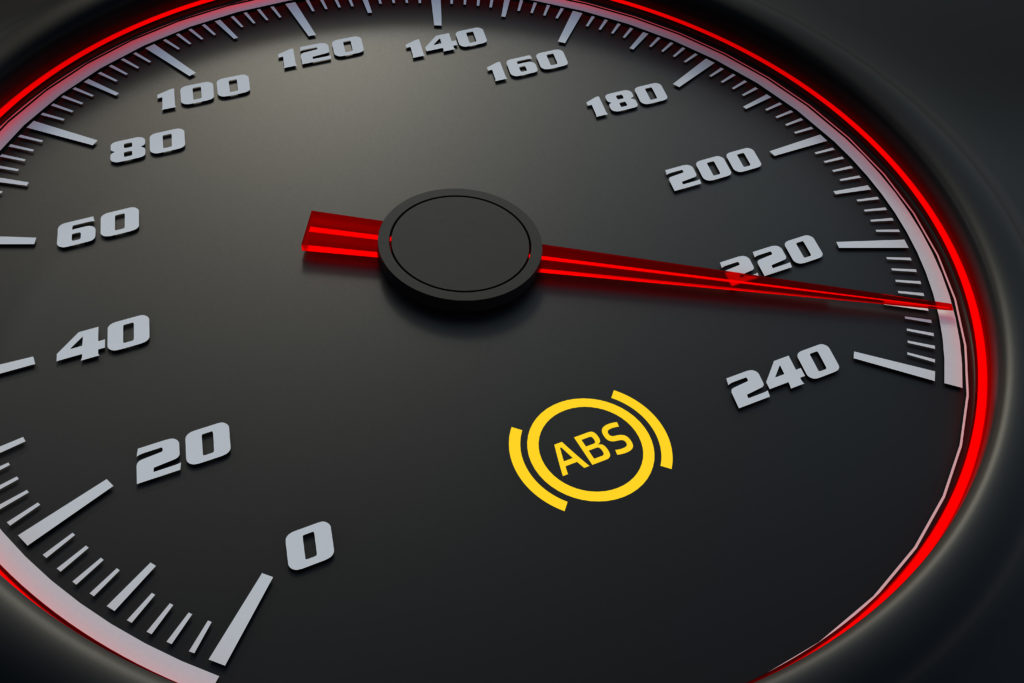
Activated ABS Warning Light
Your anti-lock braking system (ABS) warning light may also turn on if you have a bad wheel bearing. This is because the ABS sensor or encoder ring of some vehicles is integrated into the wheel hub assembly.
Whatever the cause may be, vehicle warning lights shouldn’t be ignored. Have your vehicle checked right away, so you can have the wheel bearings or any other faulty components replaced.

What is a Wheel Bearing?
Wheel bearings connect the wheels to the axle, which make them crucial components of the wheel hub assembly. They minimize friction to help the wheels rotate smoothly.
These bearings are usually held together by a metal ring. Most modern vehicles have single wheel hub assemblies, which integrate the hubs and bearings. However, on some vehicles, these two parts are considered two separate components.
The exact structure of your bearing or hub assembly will depend on your vehicle’s year, make, and model.
How Long Do Wheel Bearings Last?
In an ideal scenario, wheel bearings can last up to approximately 85,000 to 100,000 miles. But remember that this is just an estimate. Several factors can affect the lifespan of your bearings, such as their quality and the way you drive your vehicle.
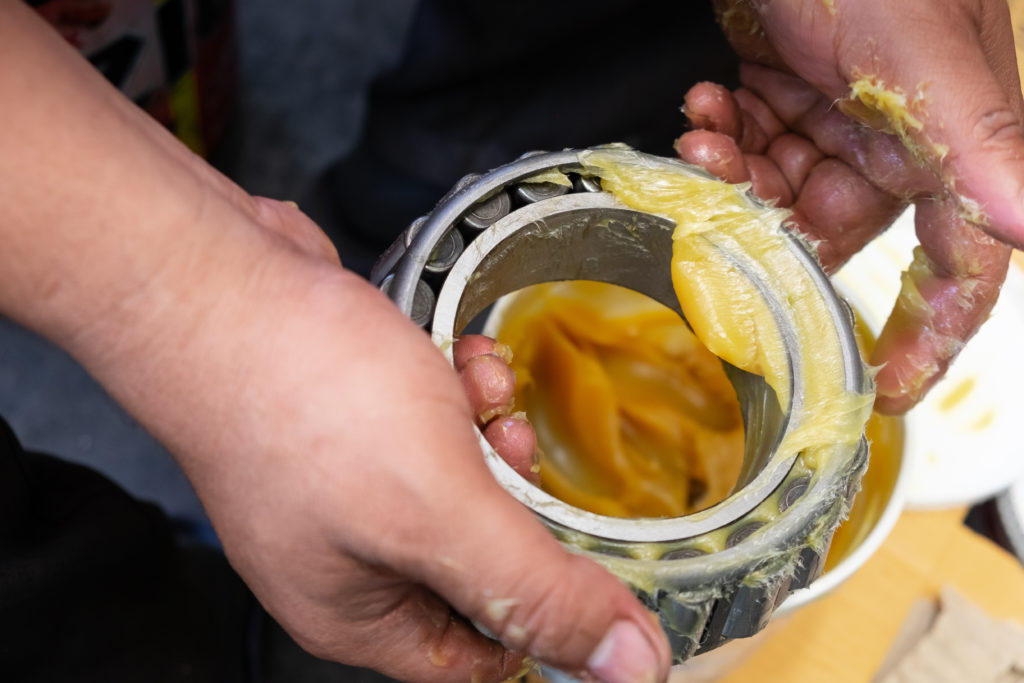

What Can Damage a Wheel Bearing?
While wheel bearings are designed to last the life of your vehicle, they aren’t invincible. They can wear and fail due to a number of reasons, such as the following:
Road Conditions
Driving over potholes and speed bumps can cause your wheel bearings to wear faster. Constantly bumping into tall curbs can also damage them. While you can’t exactly change the conditions of the roads you pass by, you can deliberatey drive slowly.
Contamination
Wheel bearings come with a seal that protects them from water, mud, and road salt. In some cases, however, these contaminants can get past the seal, contaminate the grease, and damage the bearings.
Can Custom Wheels and Tires Cause Accelerated Wheel Bearing Wear?
In some cases, yes, custom wheels and tires can cause your wheel bearings to wear faster. This is because original equipment (OEM) bearings are designed to carry specific loads, which means they won’t be compatible with every single tire out there.
While bigger and wider tires can certainly make your vehicle look cooler, they might be too heavy for your OEM wheel bearings. The added load can cause them to wear and fail faster.
When getting custom wheels, be sure to take into account the load capacity and other specifications of your vehicle’s wheel bearings.
Can I Drive With Faulty Wheel Bearings?
The short answer is no. As mentioned, driving with a bad wheel bearing is dangerous. Severely worn bearings may cause the brake rotors to wobble, resulting in reduced brake performance.
Since the tire assembly may loosen, drivers could end up losing control of the vehicle. Needless to say, this situation could cause major accidents on the road.
In extreme cases, the wheels may even come off completely.
Keep your trips safe and hassle-free by ensuring that all faulty bearings are replaced right away. Have a mechanic check your vehicle as soon as your vehicle exhibits any of the symptoms above. Replace faulty bearings if needed, so you can get back on the road in no time.
How Much Does It Cost To Replace a Wheel Bearing?
The exact price can vary depending on several factors, including your vehicle’s year, make, and model. In general, however, you can expect a wheel bearing replacement to cost anywhere between $10 and $660. If you own a luxury car, you can expect to spend a lot more as its parts tend to be more expensive.
Where to Get New Wheel Bearings for Your Vehicle
As mentioned, driving with bad wheel bearings can put you and your passenger at risk. Thankfully, you don’t have to break the bank to get high-quality replacements. You can find exactly what you need at an unbeatable price at CarParts.com.
Choose from a wide selection of competitively priced wheel bearings sourced from the leading brands in the industry. They passed stringent quality control tests, so you’re sure to get parts that are built to last.
One thing we want to provide is a high-quality online shopping experience. With our website, you can find and order the perfect wheel bearing replacements with just a few clicks.
To start, fill out our vehicle selector to narrow down the catalog to compatible bearings. Then, use the search filters to find the products that match your preferred brand, price, etc. We have a round-the-clock customer service representative, so if you have questions, don’t hesitate to contact them via our toll-free hotlines.
Check out our selection and shop now!
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.