What is an oil cooler? Oil coolers function as an extra cooling device for the engine since they create a tremendous amount of heat. Vehicle engines have cooling systems that send water or coolant through coolant channels in the engine to dissipate heat. However, engine oil also needs to be cooled because it flows around the pistons, crankshaft, and valves, which can get extremely hot because of their proximity to the combustion chamber. If engine oil heats up too much, it will lose its lubricating and cooling ability. High oil temperatures also accelerate oil breakdown, causing engine oil to turn into sludge and deposits and cause a wide range of engine issues.
What Does an Oil Cooler Do?
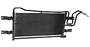
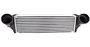
The oil cooler is responsible for keeping the oil within its ideal operating temperature, which is around 230 to 260 degrees Fahrenheit. Oil coolers are essentially heat exchangers, which are components that function similarly to a vehicle’s radiator. These components are designed to have a lot of surface area, so that they can radiate as much heat as possible to the surrounding air or coolant, depending on the type of oil cooler. Oil-to-air oil coolers are typically located behind the vehicle’s grilles, near its radiator. This location provides the maximum amount of airflow, which is necessary for heat to dissipate effectively.
How Does an Oil Cooler Work?
There are two types of oil coolers. There are oil-to-water oil coolers and oil-to-air oil coolers.
Oil-to-Water Oil Coolers
Hot oil that comes from the engine block is fed through the oil cooler’s tubes. Engine coolant or water from the vehicle’s cooling system flows around these tubes. The oil heats up the tubes and this heat is absorbed by the surrounding coolant or water. This coolant is then directed to the vehicle’s radiator, which dissipates the heat using air.

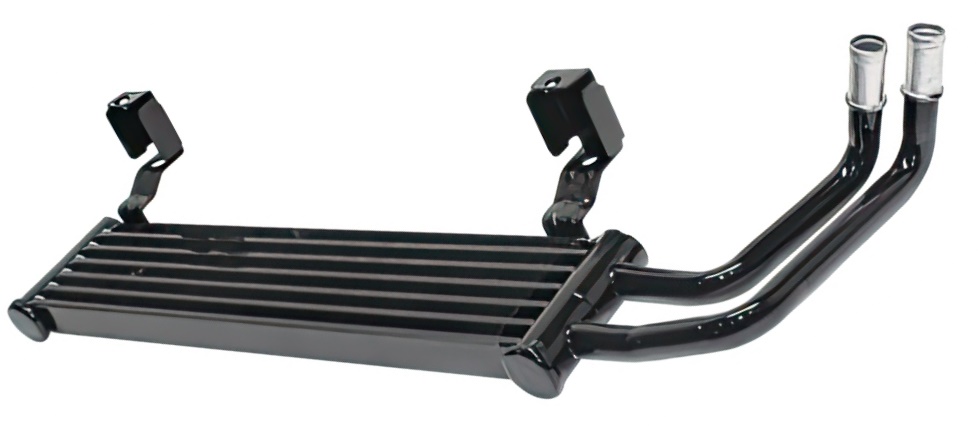
Oil-to-Air Oil Coolers
These oil coolers work similarly to the vehicle’s radiator. The oil is sent to the heat exchanger, which is a set of thin tubes that have many thin metal fins connected to them. The thin tubes and metal fins allow heat to quickly dissipate through the surrounding air. These oil coolers will leak oil onto the ground but won’t leak oil into the coolant.

Faulty Oil Cooler Symptoms
Oil coolers in cars wear out over time and can eventually fail. When this happens, your vehicle will show several possible symptoms such as the following:
Oil Leaks
An oil cooler adapter connects the engine’s oil lines to the oil cooler. If the oil cooler adapter or the o-ring that connects the oil cooler to the adapter is damaged, then oil can leak out of the engine and create puddles under your vehicle. The oil cooler can also leak oil.
Having an oil cooler that leaks is a serious issue because it can cause low oil levels, which will deprive your engine of oil’s lubricating and cooling properties. Eventually, low oil levels can cause your engine to overheat or even seize. If you notice oil leaking from your vehicle, we recommend that you reach out to a trusted mechanic so that they find where the leak is coming from and seal it off immediately.

Coolant Leaks
Since oil-to-water oil coolants use oil or water, a damaged oil cooler can leak coolant. When this happens, your vehicle’s coolant reserves can get low. This can cause your vehicle to overheat.
An overheating engine will cause pistons to warp, gaskets to leak, and can even crack the engine block. The engine might also make horrible knocking and grinding noises. If kept running, the engine can get severely damaged or seize.
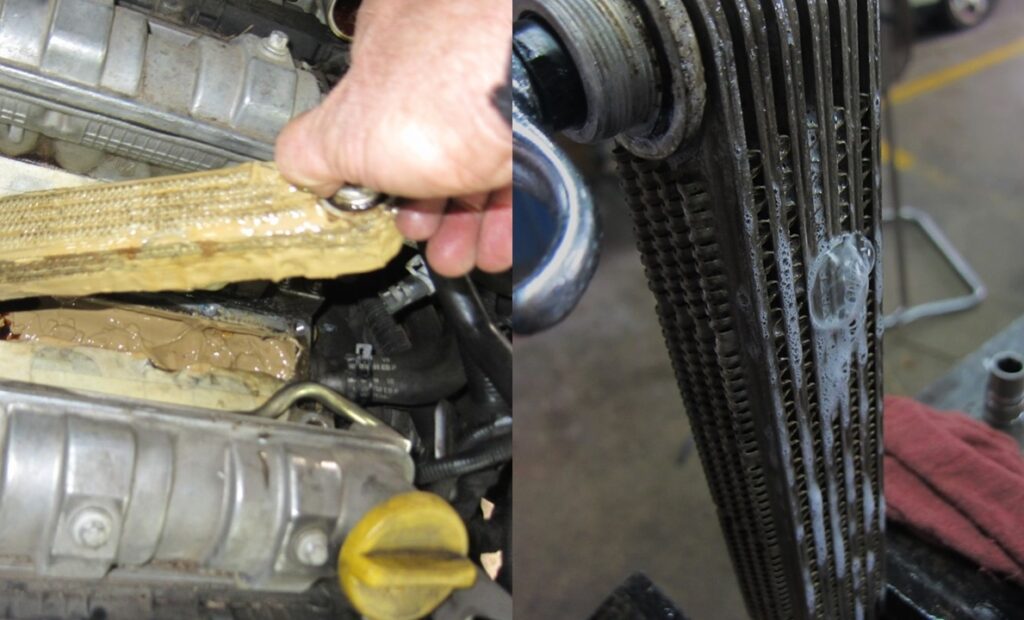
Oil Mixing With Coolant
The oil cooler is designed to contain both oil and coolant in separate compartments. A damaged oil cooler can develop small internal cracks that can cause oil and coolant to mix.


The coolant in your reservoir will turn into a thick, discolored fluid that resembles gravy if it’s mixed with oil. Similarly, your engine’s oil will also change its color and consistency.

Illuminated Warning Lights
Most modern vehicles come with sensors that can detect engine oil and cooling system problems. If the oil cooler fails, it can cause warning lights to illuminate on the dashboard. These can include the check engine light, the oil pressure warning light, and the engine temperature warning light. If you see any warning lights on your dashboard, you ask an experienced mechanic to inspect your car.
Strange Noises
A faulty oil cooler can also cause strange noises like knocking, ticking, or rattling. These noises could suggest severe engine damage as a result of low oil or coolant levels. You might also feel excess vibrations from your vehicle.
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.





























This is so helpful and educative. Thank you