The suspension system consists of different parts and components that improve ride comfort. Suspension systems all have a limit of travel, so if a vehicle hits a pothole or a bump on the road, the wheels will be forced upwards with a lot of force. The springs usually absorb most of this impact, but they can be pushed to their mechanical limit, especially if the vehicle runs over a large bump.
What are Bump Stops?
A rubber or urethane bump stop is installed to avoid metal-to-metal contact between suspension system components and the vehicle frame. Also called a suspension bumper, strike-out bumper, or jounce bumper, the bump stop provides additional protection and shock absorption, especially when the suspension system bottoms out. Bump stops also allow vehicle owners to install longer shocks.
In reality, bump stops only come into play in extreme situations. It depends a lot on the style of driving and the prevailing terrain where the vehicle typically travels. (Note: There are some stops that don’t have cushioning, such as steering stops. These places need a bit of grease smeared on them to prevent noisy scraping sounds during sharp turns when going over rough ground.)
There are some stops that don’t have cushioning, such as steering stops. These places need a bit of grease smeared on them to prevent noisy scraping sounds during sharp turns when going over rough ground.
–Richard McCuistian, ASE Certified Master Automobile Technician
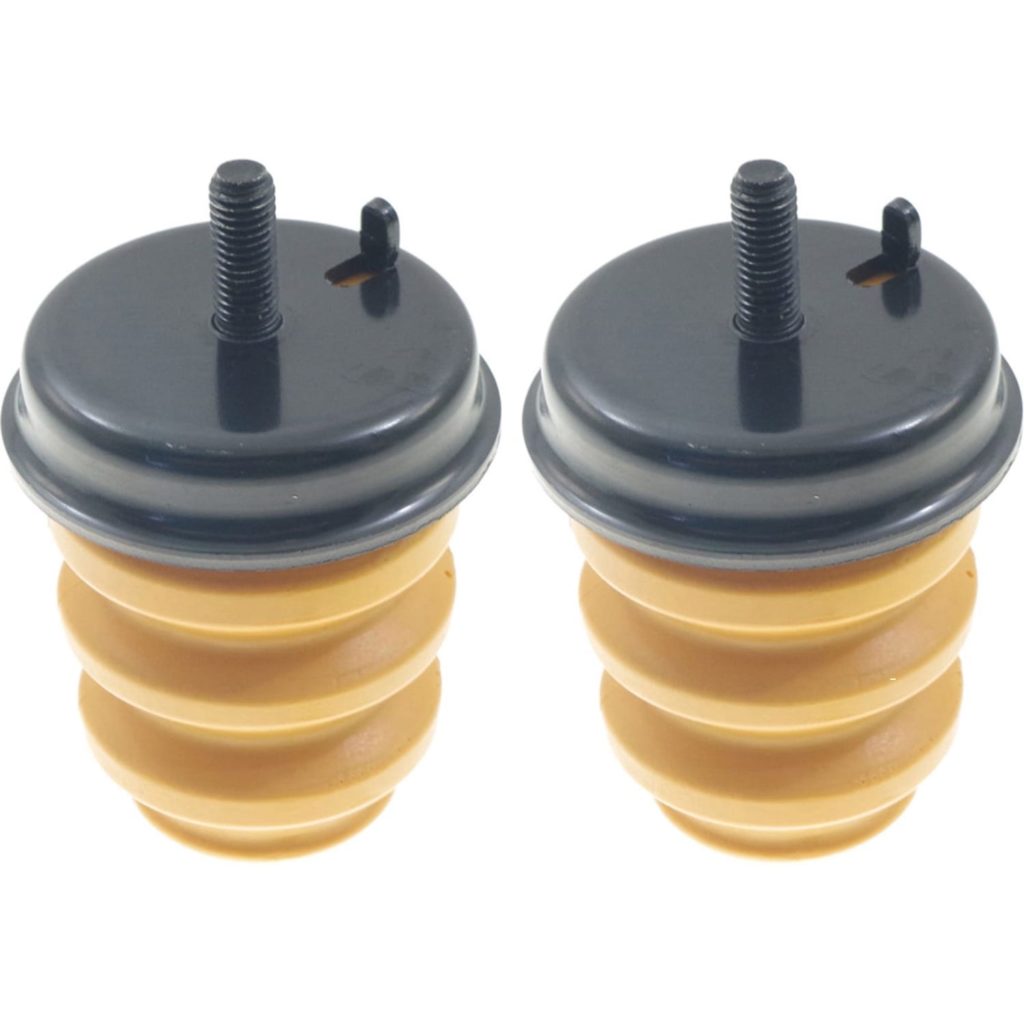

Bump stops are often overlooked, but are actually critical in maintaining comfortable and quiet suspension system function. Read on to learn more about how to spot bad bump stop symptoms, what causes them to fail, and when to replace them.
What are the Signs of a Bad Bump Stop?
While bump stops are made with durable materials like rubber and urethane, they may disintegrate or get damaged over time. However, while bump stops are important, they may not be important enough to take the vehicle out of service in those cases where they’re missing or severely damaged.
Nevertheless, you should include bump stops in your regular maintenance checks. These are the two most common symptoms of a faulty bump stop:
Unusual Noises
When bump stops deteriorate, there’s nothing to prevent suspension system components from hitting the frame or the tires from hitting the fender of the vehicle. As a result, you may hear unusual banging noises whenever you hit a bump or a pothole on the road, or when you’re carrying a heavy load. This isn’t the kiss of death or anything, but it can be dreadfully unpleasant.
Excessive Vibration
Another result of increased metal-to-metal contact caused by faulty bump stops is excessive vibration. Once your vehicle’s bump stops fail, you may notice that your ride is shaky and uncomfortable, especially when driving on uneven roads.

Note, however, that this symptom doesn’t necessarily indicate a bad bump stop since bump stops only make contact with extreme suspension movement over rough terrain. During normal driving, bump stops aren’t in play.
How Does a Bump Stop Fail?
Shocks and springs work together to absorb the impact of vertical bumps. Suspension springs absorb most of the impact, while the shocks absorb minor impact and ensure that the tires are on the road at all times.
Sagging springs and defective shocks can allow excessive suspension bounce, which tends to put most of the damping effort on the bump stop, causing it to wear out faster and eventually fail.
When Should You Replace Your Old Bump Stop?
Once you notice one or more of the symptoms listed above, you should check to see if a bad bump stop really is the root cause of the issue. Once you’ve confirmed that the bump stop has degraded or is damaged, it’s time to get a replacement. This is primarily to avoid suspension system damage. While the suspension system is designed to work with or without bump stops, missing bump stops can cause annoying sounds you’d rather do without if you frequently drive on rough terrain.
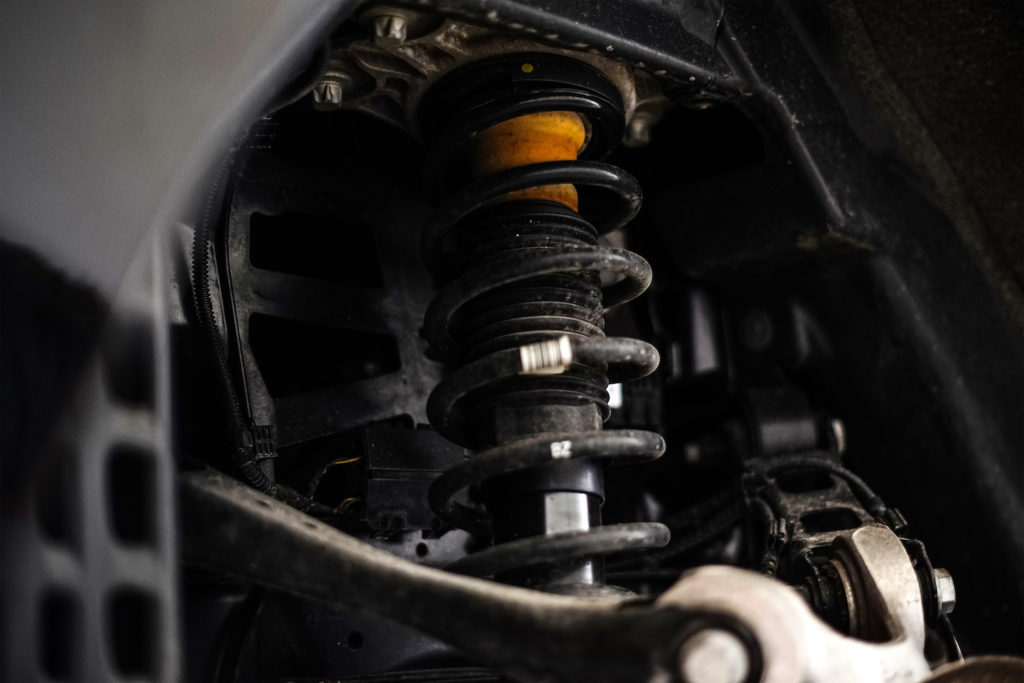

Some struts come with their own replacement bump stops if you buy the assembled unit rather than just the strut shock. This may be the best way to go anyway, since you should get new springs and strut mounts along with the shock absorber itself.
To ensure that your bump stops are in top shape, it’s a good idea to include them in your routine maintenance checks. This way, you may be able to spot cracks or other signs of damage and replace the bump stop right away.
How Much is a Bump Stop Replacement?
The price of aftermarket bump stop replacements can range from $7 to $780 for the part itself. Expect to pay more for professional installation. This price range depends on the brand, series, and quantity of specific bump stops. However, other factors such as bump stop type and material may also affect the pricing.
Before purchasing a replacement bump stop, make sure to note the quantity that you need. Bump stops are typically sold individually, although they also come in sets of two to four pieces. Bump stop kits are also available.
CarParts.com has a wide selection of replacement bump stops and other aftermarket suspension system components for all kinds of vehicle makes and models, as well as all kinds of applications—so you can be sure to find the right parts for your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions About Bump Stops
Where is the Bump Stop Located?
There are several different locations where bump stops can be mounted, and it may be tricky to locate them. Many bump stops are found in line with the vehicle’s shock or piston rods. This location allows the bump stops to absorb more force, especially when the shock reaches its limit.
Another possible bump stop location is between the axle and frame. These are called axle snubbers, and they absorb the impact that may cause the axle to hit against the frame.
Are There Different Types of Bump Stops?
Bump stops come in a wide variety of designs and materials. Urethane and rubber bump stops are the most common and popular types.

There are also hydraulic bump stops that work like your average shocks.
When shopping for a replacement bump stop, make sure that the type you get is made specifically for your vehicle’s year, make, and model, preferably one with an OE-design. Doing so ensures a hassle-free installation and minimizes the risk of damaging nearby suspension system components.
Are Bump Stops Necessary?
Yes, bump stops are necessary if your driving routes are as previously described. Bump stops’ main function is twofold. First, the primary function of a bump stop is to ensure a smooth and comfortable ride. If you don’t have bump stops installed, it’s not going to be a very comfortable ride for you and your passengers.
Second, by not installing bump stops, you put your suspension and steering system components at risk of accelerated wear. Suspension parts, such as shocks or struts, will have to make up for the lack of added cushioning provided by the bump stops. Thus, these components may give out before the end of their service life.
Can You Drive Without Bump Stops?
It’s possible to drive without bump stops, but it’s not advised for both practical and safety reasons.
Where to Find Bump Stops for Your Vehicle
Bad bump stops can cause unusual noises when driving over bumps on the road. It can also cause excessive vibration, making your ride uncomfortable. Luckily, it’s easy to shop for a replacement bump stop here at CarParts.com.
All you have to do is use our vehicle selector and check out the bump stops that are compatible with your ride. You can also use our search filters to narrow down your search according to your preferred brand or price range.
Our bump stops are sourced from well-known brands that manufacture parts to meet OE specifications in world-class facilities. And the best part is that these products come with a low-price guarantee.
Do you have questions about fitment or shipping? Our hotline is open 24/7 for your queries. Check out our catalog and order today!
Products Mentioned in this Guide
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.

 Coil Spring
Coil Spring
 Shock And Strut Mount
Shock And Strut Mount
 Bump Stop
Bump Stop
 Shock Absorber And Strut Assembly
Shock Absorber And Strut Assembly