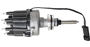
Ballast resistors play an important role in a vehicle’s ignition system. They’re responsible for lowering the voltage received by the ignition coils from the battery.
While ballast resistors are mostly no longer present in modern vehicles because of electronic ignition systems, there were some electronic ignition systems that were equipped with ballast resistors. One notable exception was Ford. Fords didn’t use a ballast resistor, but used a resistor wire that was built into the harness between the ignition switch and the coil positive feed.

What Does a Ballast Resistor Do?
The ballast resistor drops voltage between the ignition switch and the ignition coil’s positive wire so that only about 8 volts is delivered to the ignition coil when the ignition switch is in the “run” position.
In the “start” position, a full 12 volts is delivered to the ignition coil, bypassing the resistor. This is why older solenoids have an “S” terminal for the solenoid and an “I” terminal for bypassing the ballast resistor during start. Older GM starter solenoids had the same two terminals for the same reason.
The 12 volts of power supplied by vehicle batteries is typically too much power for the vehicle’s ignition coils. When vehicles had contact points, running the system with the ballast resistor bypassed (as some people would do when it burned out), would burn up the contact points in the distributor in a very short period of time.
Before the introduction of ballast resistors, ignition coils used to overheat and require frequent replacement in trucks.

The ballast resistor regulates the current flowing to the ignition coil by dropping it 3 to 4 volts, so that it operates at peak performance and has a longer lifespan. Without the ballast resistor, the ignition coils can overheat and wear out faster.
Ballast resistors can be made of a variety of materials, including carbon, wound wire, or metal oxide, depending on the particular application and circuit requirements. They’re generally rated in Ohms and Wattage, which indicate their resistance and power-handling ability.
Bad Ballast Resistor Symptoms
Like any electronic component, ballast resistors degrade over time due to normal wear. If the ballast resistor fails, it can cause a number of symptoms that can affect your vehicle’s reliability and performance.
Start-and-Die
Since the ballast resistor is bypassed by voltage from the solenoid “I” terminal during engine start, a burned out ballast resistor can cause the engine to start initially. When the starter solenoid stops providing the bypassed voltage to the coil, the ignition system stops providing spark, resulting in a start-and-die issue.
Rough Idle/Misfires
A defective ballast resistor can cause misfiring or harsh idling but only if it has developed more resistance and has reduced the available voltage to the ignition coil to the point that the coil can’t fire as it should. Ordinarily, the resistor doesn’t cause this problem. A weak spark is typically a problem with the ignition coil.
Stalling
A faulty ballast resistor might not allow enough voltage to reach the spark plugs and cause a weak or inconsistent spark, which can lead to your engine stalling.

Premature Ignition Coil Failure
A defective ballast resistor can overheat the ignition coil, resulting in premature failure. Note, however, that this only happens if the resistor is internally shorted so that it has no resistance at all, which is very rare. Usually, an older resistor will, if it changes, develop more resistance, and not less.
Premature failure only happens if the ballast resistor is internally shorted so that it has no resistance at all, which is very rare. Usually, an older resistor will, if it changes, develop more resistance, and not less.
–Richard McCuistian, ASE Certified Master Automobile Technician
If your vehicle’s ballast resistor causes the ignition coil to fail, then it can show similar symptoms like misfires and difficulty starting. A faulty ignition coil can also cause additional issues such as an illuminated check engine light, poor fuel economy, reduced power, and backfires.
Diagnosing a faulty ballast resistor typically involves using a multimeter to check whether the resistor is functioning as it should.
However, this task can be difficult if you aren’t experienced in DIY repairs. If your vehicle is showing these symptoms, you should head to a trusted mechanic.

Getting Your Hands on a New Ballast Resistor
Driving with a bad ballast resistor can negatively affect your vehicle’s performance. Luckily, you can easily get a replacement that’s compatible with your vehicle thanks to CarParts.com.
The best part? You don’t even have to take one step outside your door to get your hands on a new ballast resistor. All you need to do is go online and visit our website. Simply input the exact year, make, and model to browse through compatible parts for your vehicle.
All products in our catalog are sourced from some of the most reliable names in the industry. And because we stand by their quality, we offer 60-day return and lifetime replacement guarantees.
Don’t let a malfunctioning ballast resistor ruin your next trip. Check out our selection of quality auto parts today!
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.