Your vehicle’s fuel level is probably one of the first things you check as soon as your dashboard lights up. It’s the indicator that determines how far your car can go without making a quick trip to the gas station.
Even rookie drivers know the principle of the fuel level gauge一“E” stands for “empty,” and “F” stands for “full.”
It might seem like a simple concept, but there’s actually a lot of activity that goes on inside the fuel tank and sending units for the gauge to display accurate readings.
For example, some old Volkswagen bugs had a short cable leading from a mechanical float inside the tank to the gauge on the dash.
How Does a Fuel Gauge Work?
The operation of a fuel gauge depends on its type, which can either be analog, electronic, or magnetic.
Analog Fuel Level Gauge
An indicator needle typically represents the fuel level in an analog setup. A heated bimetal strip moves this needle once current flows through it.
The bimetal strip can control the needle because of a small voltage regulator inside the instrument panel. The fuel tank sending unit provides a ground circuit for the fuel gauge and controls the amount of current that flows through it.
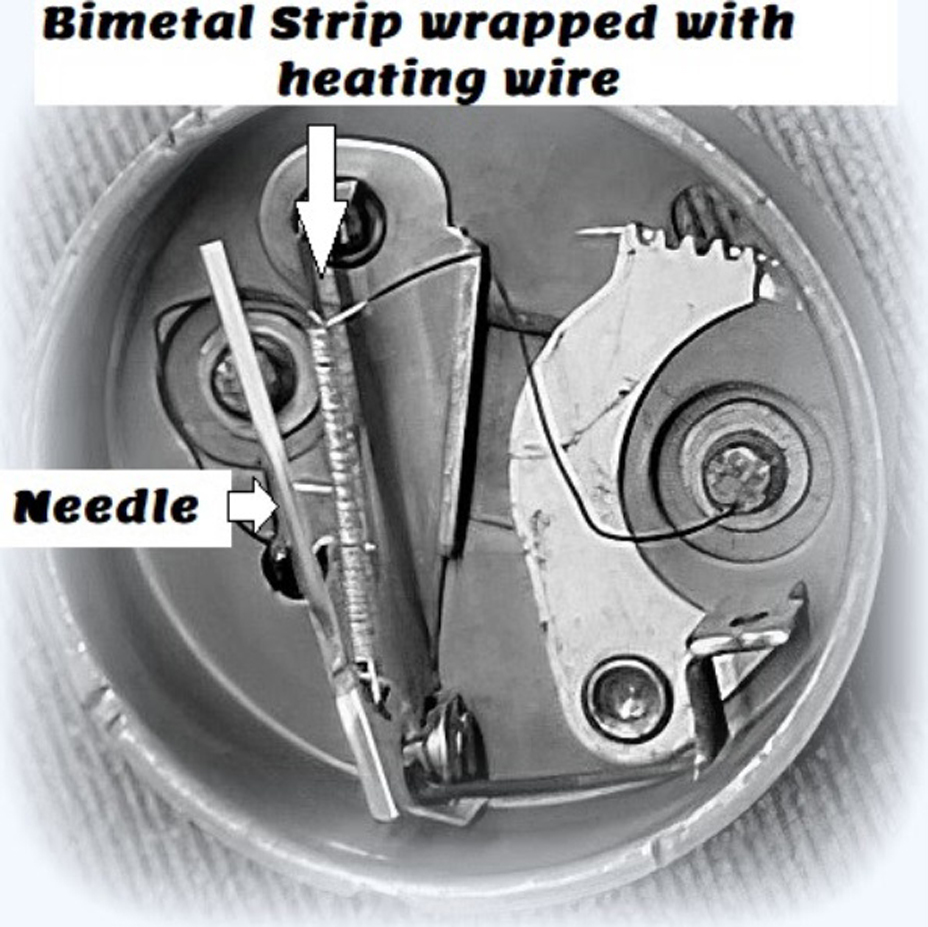
The movement of the indicator needle represents the activity that occurs in the fuel tank that contains a variable resistor.
As the fuel level changes, so does the resistance of the fuel tank sending unit. As the sending unit delivers more ground to the heating wire in this type gauge, the bi-metal strip will change shape and move the needle.
This kind of gauge began to be replaced with magnetic style gauges in the early 1970s but remained on some vehicles into the 1980s.
Magnetic Fuel Level Gauge
A magnetic fuel level gauge uses small electromagnetic coils that are connected to a sending unit to display information on fuel level. The same mechanism is used to display other data, such as water temperature and oil pressure.
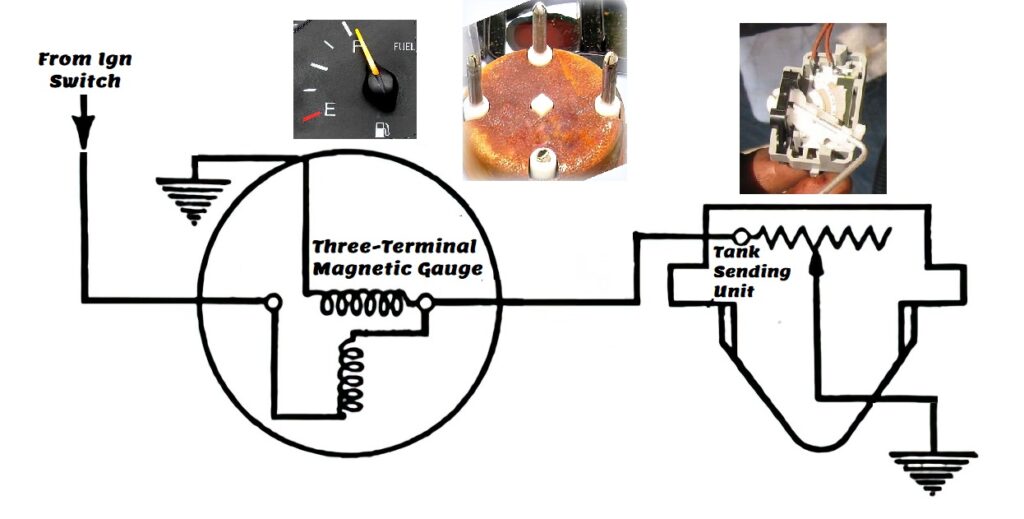
A magnetic fuel level gauge is more accurate than resistance-type gauges.
In terms of its schematic, the needle should point to “E” if the sensor wire is unplugged and grounded. Meanwhile, the needle should point to “F” if the sensor is unplugged or away from ground.
All gauges use similar sensors regardless of their type. An electronic control unit also operates these gauges and sends information to the powertrain control module (PCM) for engine data.
Instrument clusters on newer vehicles, even if they have needle type gauges, are connected to the vehicle network (class 2, CAN bus, PCI bus, etc.) and have a computer or a chip as part of the instrument cluster, so that a small servo drives each needle based on the input received through the CAN bus or directly received by the computer on the instrument cluster circuit board.
Electronic Fuel Level Gauge
An electronic fuel level gauge works the same way as the analog type. The only difference is that an electronic gauge displays fuel level information using numbers or a bar graph instead of an indicator needle.
What Causes the Fuel Gauge to Fail?
A gas gauge that’s stuck on full even after you’ve driven for some time is usually a telltale sign that something’s wrong with it.
Sending units can wear out; they don’t always, but they can. This is a very common failure on 2000s vintage GM vehicles.
As an oddity, some Ford minivans in the late 2000s had a rear end control module that would receive input from the gauge and send it to the cluster. If the gauge unit failed, the most recent dependable reading would be sent to the cluster.
There’s typically a “slosh” function to prevent the fuel gauge needle from moving around as gas sloshes in the tank, but it works different on every platform.
A faulty gauge can also display an empty fuel level reading even when there’s still a lot of gas left. In some cases, the indicator can get stuck somewhere in the middle.
There are several reasons why your fuel level gauge is not working as it should, such as:
- Poor ground connection
- Wiring issues between the gauge and fuel sending unit
- Defective voltage supply to the gauge
There are, however, some instances where you can rule out these causes.
For example, if the temperature and oil pressure gauges are malfunctioning together with the fuel level gauge, the problem is usually a faulty instrument voltage regulator or an issue with the instrument panel wiring.
Fuel Gauge Reset
Vehicles with an indicator needle might need to have their fuel gauges reset if the needle didn’t change its position after you topped up on fuel. This usually happens when you run out of fuel.
To reset the fuel level gauge, you might have to remove the battery’s negative cable connection from the terminal and disconnect the wire that links the gauge to its sending unit.
Then, connect the detached wire to a metal surface on your vehicle for grounding purposes. Doing so should have your fuel gauge needle moving again.
Low Fuel Level Warning Light
Most vehicles usually have a low fuel level warning light wired to the fuel gauge.
The warning light is triggered whenever the fuel gauge falls below a certain level, depending on the vehicle’s model.
For example, some Fords activate this warning light if the gauge reads below 1/4 full. Meanwhile, the warning light turns on when there’s only one to two gallons of fuel in the tank for late-model electronic fuel level gauges.
Fuel Gauge FAQs
Below are the answers to some of the frequently asked questions (FAQs) about the fuel level gauge.
How Long Does a Fuel Level Gauge Last?
Fuel level gauges should last the lifespan of your vehicle. However, there might be some instances where it can fail prematurely. It can also malfunction if a connected part like the sending unit is damaged.

Can I Drive With a Defective Fuel Gauge?
A damaged fuel level gauge won’t affect your engine. In fact, your car will run the same way without it.
However, driving with a broken fuel gauge means you have no information about how much fuel is left in your tank. That can be dangerous because you might get stranded in the middle of nowhere.
Make sure to have your fuel level gauge repaired or replaced as soon as possible.
How Accurate is a Fuel level Gauge?
According to the American Automobile Association (AAA), fuel level gauge readings aren’t exactly 100% accurate.
Experts say that these readings are more of an estimate and that it’s best to fill up on gas when there’s about a quarter left in the tank.
How Much Does a Fuel Level Gauge Replacement Cost?
Replacing a damaged fuel level gauge can cost anywhere between $50 and $150. Factors that affect the price typically include the brand and your vehicle’s specifications (year, make, and model).
How Do I Replace My Car’s Fuel Level Gauge?
Replacing your vehicle’s damaged fuel level gauge requires certain equipment and extensive knowledge of automotive wiring.
If you’re a seasoned DIYer who knows their way around vehicle repair, make sure to have a set of vehicle-specific instructions before proceeding. Otherwise, you can always bring your vehicle to the nearest repair shop to have a professional mechanic do the job for you.
Where to Get a Fuel Gauge Replacement for Your Ride
It’s important to know how much fuel is in your tank. Swiftly replace your faulty fuel gauge once you confirm it’s faulty. Don’t let inaccurate readings or a malfunctioning gauge disrupt your driving experience. Order a new one online from CarParts.com.
We offer a wide selection of fuel gauges sourced from top aftermarket brands. They’re all screened by our team of industry experts to ensure they match or exceed our quality standards.
Need to get back on the road as soon as possible? Skip the lengthy wait times for crucial parts. Order from us, and expect your part to be delivered in just a few days. That’s because we have warehouses strategically located nationwide to ensure fast shipping.
Visit our website, and explore our extensive catalog of fuel gauges compatible with various vehicles. You can use our search filters to narrow down choices by the brand or price range you prefer.
Check out our selection, and order your replacement fuel gauge today!
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.

















