Answers

Oct 22, 2023 - 10:08 AM
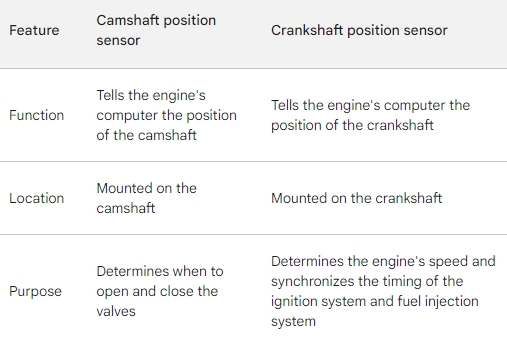
Both the camshaft position sensor (CMP) and crankshaft position sensor (CKP) are essential components in modern vehicles, especially in Ford vehicles. They both provide vital information to the engine control module (ECM) to control various functions of the engine. Here's a brief comparison:
**Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP):**
1. **Location:** Located on the camshaft, often on the cylinder head.
2. **Function:** Monitors the position and rotational speed of the camshaft.
3. **Purpose:** Helps control fuel injection and spark timing. Also plays a role in variable valve timing systems (if equipped).
4. **Symptoms of Failure:** Rough idling, poor acceleration, stalling, decreased fuel efficiency, and the engine may not start.
**Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP):**
1. **Location:** Located on the engine block or the transmission bell housing, adjacent to the crankshaft.
2. **Function:** Monitors the position and rotational speed of the crankshaft.
3. **Purpose:** Provides the ECM with information about the position of the pistons in relation to the engine's rotation. This is crucial for determining when to fire the spark plugs and control fuel injection.
4. **Symptoms of Failure:** Engine misfires, stalling, no start condition, erratic behavior like sudden jerking or poor acceleration, and decreased fuel efficiency.
**In the context of Ford vehicles:**
Both sensors play crucial roles in modern Ford engines for optimal performance and efficiency. Problems with these sensors in a Ford vehicle can trigger the check engine light, and diagnosis using a scanner can often pinpoint which sensor might be the cause. Proper maintenance and timely replacement can prevent potential engine issues.
**Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP):**
1. **Location:** Located on the camshaft, often on the cylinder head.
2. **Function:** Monitors the position and rotational speed of the camshaft.
3. **Purpose:** Helps control fuel injection and spark timing. Also plays a role in variable valve timing systems (if equipped).
4. **Symptoms of Failure:** Rough idling, poor acceleration, stalling, decreased fuel efficiency, and the engine may not start.
**Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP):**
1. **Location:** Located on the engine block or the transmission bell housing, adjacent to the crankshaft.
2. **Function:** Monitors the position and rotational speed of the crankshaft.
3. **Purpose:** Provides the ECM with information about the position of the pistons in relation to the engine's rotation. This is crucial for determining when to fire the spark plugs and control fuel injection.
4. **Symptoms of Failure:** Engine misfires, stalling, no start condition, erratic behavior like sudden jerking or poor acceleration, and decreased fuel efficiency.
**In the context of Ford vehicles:**
Both sensors play crucial roles in modern Ford engines for optimal performance and efficiency. Problems with these sensors in a Ford vehicle can trigger the check engine light, and diagnosis using a scanner can often pinpoint which sensor might be the cause. Proper maintenance and timely replacement can prevent potential engine issues.
Oct 23, 2023 - 12:18 PM
The camshaft sensor gives information about the camshaft which basically serves, with other parts to open and close the valves in the cylinder head. The crankshaft position sensor gives positioning information about the crankshaft which with other parts moves the pistons up and down in the cylinders of the engine block.
Nov 07, 2023 - 11:39 AM
The camshaft position sensor (CMP) and crankshaft position sensor (CKP) are both crucial components of a vehicle's engine management system. While they may sound similar, they serve different purposes:
1. Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP): The CMP sensor monitors the position and speed of the camshaft(s). It provides vital information to the engine control module (ECM) to synchronize fuel injection, ignition timing, and valve timing. By detecting the position of the camshaft, the CMP sensor helps the ECM determine the optimal timing for fuel injection and ignition.
2. Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP): The CKP sensor monitors the position and speed of the crankshaft, which is responsible for converting linear motion into rotational motion. The CKP sensor provides data to the ECM, allowing it to determine the position of the pistons and the crankshaft's rotational speed. This information is critical for several engine functions, including fuel injection timing, ignition timing, and overall engine performance.
1. Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP): The CMP sensor monitors the position and speed of the camshaft(s). It provides vital information to the engine control module (ECM) to synchronize fuel injection, ignition timing, and valve timing. By detecting the position of the camshaft, the CMP sensor helps the ECM determine the optimal timing for fuel injection and ignition.
2. Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP): The CKP sensor monitors the position and speed of the crankshaft, which is responsible for converting linear motion into rotational motion. The CKP sensor provides data to the ECM, allowing it to determine the position of the pistons and the crankshaft's rotational speed. This information is critical for several engine functions, including fuel injection timing, ignition timing, and overall engine performance.


Nov 11, 2023 - 05:43 PM
- the camshaft position sensor reads the camshaft as well as being responsible for the ignition coils firing in the right sequence. The crankshaft position sensor reads the crankshaft position and is responsible for the injectors firing. Together they give the omputer the base engine timing. The ecm can adjust timing curve depending on accelerator pedal position and torque demand





Add New Comment